Meteorites Trigger Avalanches on Mars
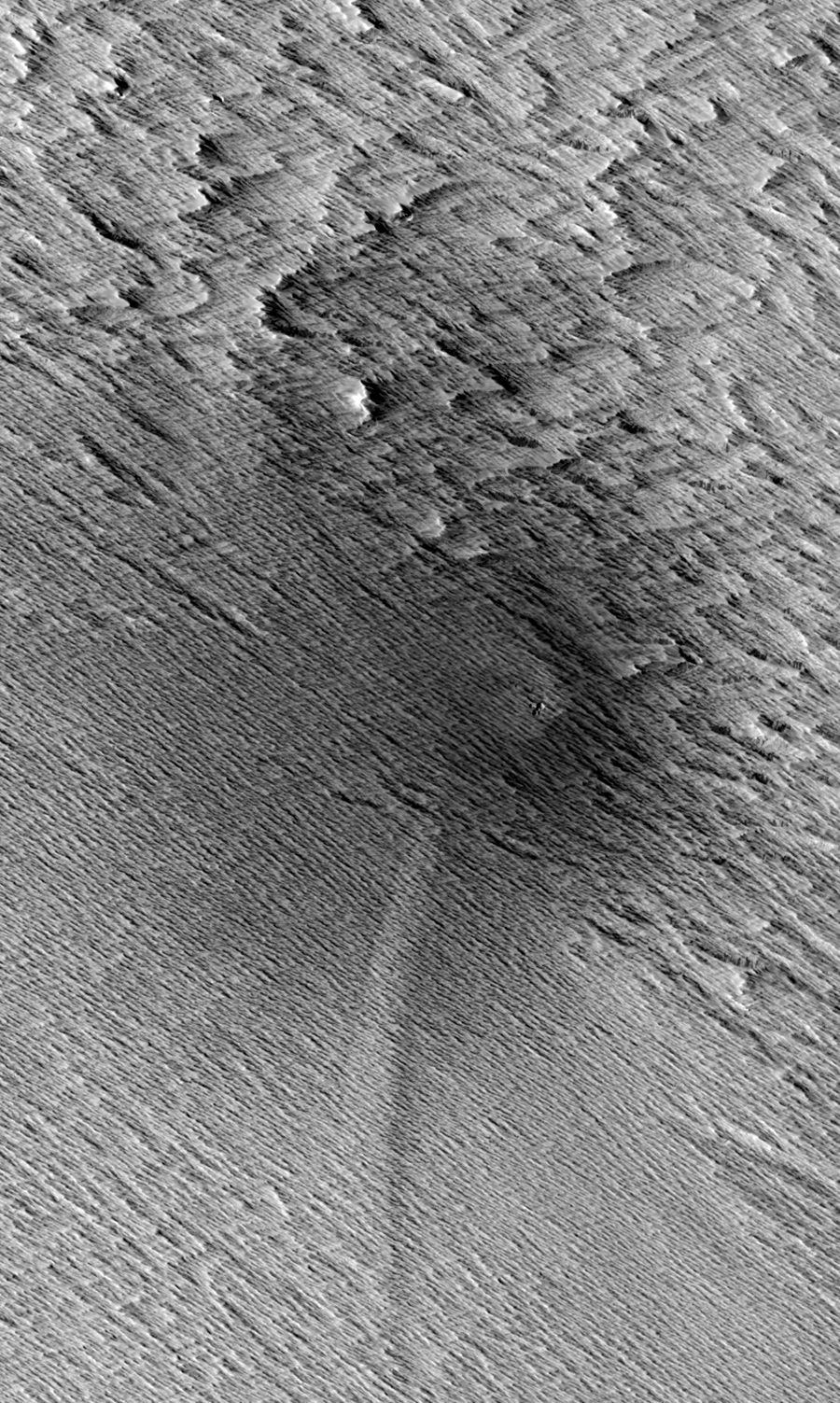

As meteorites careen toward the surface of Mars, they can trigger avalanches before they even hit the ground, a new study suggests.
Space rocks flying toward the Martian surface can travel at several times the speed of sound, creating shockwaves in the air. These shockwaves pummel the ground, kicking up dust that rolls over slopes in dark streaks that can be seen from orbit, scientists say.
"We expected that some of the streaks of dust that we see on slopes are caused by seismic shaking during impact," said University of Arizona undergraduate student Kaylan Burleigh, who led the research project, in a statement. "We were surprised to find that it rather looks like shockwaves in the air trigger the avalanches even before the impact."
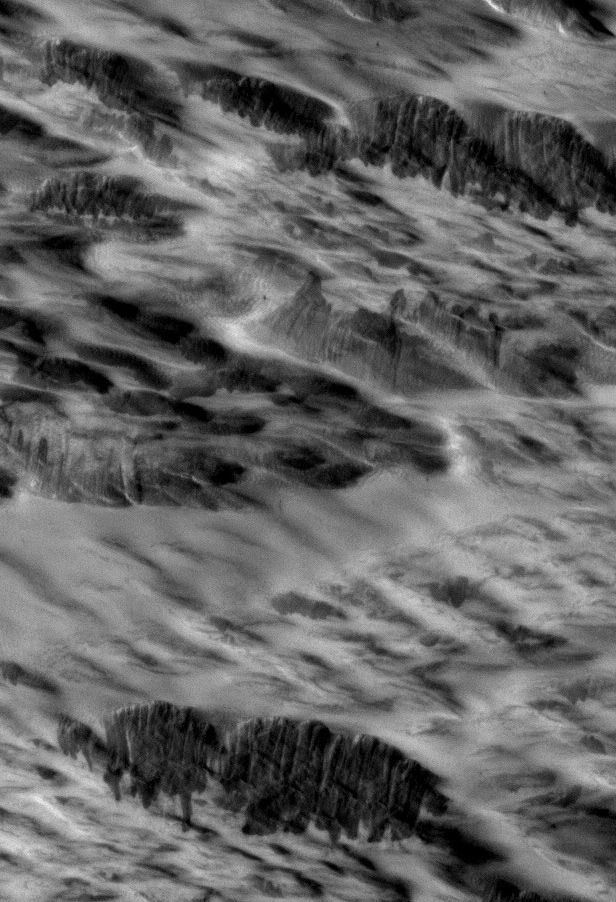
Burleigh and other researchers analyzed dark streaks seen in images from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, and found that many did not fit the pattern expected if they were caused by the seismic shaking produced by the impact of a space rock. Instead, these streaks bore signatures of shockwaves that would have been created before any impact occurred.
Indeed, when the scientists used a computer model to simulate the geologic features expected from such shockwaves, they found characteristic curved marks, called scimitars, exactly matching those seen on the surface of Mars.
"Those scimitars tipped us off that something other than seismic shaking must be causing the dust avalanches," Burleigh said.
Mars is regularly barraged with meteorite impacts. The planet's thin atmosphere is 100 times less dense than that of Earth and cannot shield the surface from even small space rocks.
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
On average, scientists spot about 20 new impact craters between 3 and 165 feet (1 and 50 meters) wide every year.
"This is one part of a larger story about current surface activity on Mars, which we are realizing is very different than previously believed," said Alfred McEwen, principal investigator of the HiRISE (High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment) camera on the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, and one of the co-authors of the new study. "We must understand how Mars works today before we can correctly interpret what may have happened when the climate was different, and before we can draw comparisons to Earth."
You can follow SPACE.com assistant managing editor Clara Moskowitz on Twitter @ClaraMoskowitz. Follow SPACE.com for the latest in space science and exploration news on Twitter @Spacedotcom and on Facebook.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.

Clara Moskowitz is a science and space writer who joined the Space.com team in 2008 and served as Assistant Managing Editor from 2011 to 2013. Clara has a bachelor's degree in astronomy and physics from Wesleyan University, and a graduate certificate in science writing from the University of California, Santa Cruz. She covers everything from astronomy to human spaceflight and once aced a NASTAR suborbital spaceflight training program for space missions. Clara is currently Associate Editor of Scientific American. To see her latest project is, follow Clara on Twitter.
