Sojourner: The first successful Mars rover
Mars Pathfinder carried the first rover to Mars, using an innovative airbag landing system to bounce safely onto the surface.
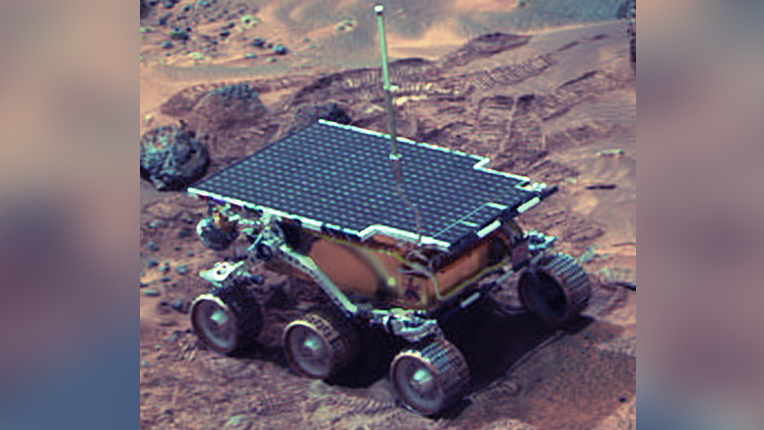

The Mars Pathfinder mission marked a groundbreaking moment in NASA's exploration of Mars, paving the way for future rover missions.
Launched on Dec. 4, 1996, and landing on July 4, 1997, the mission successfully delivered the first rover, Sojourner, to the Martian surface via the Pathfinder lander.
One of its most notable innovations was the unique landing system. Instead of relying on traditional rocket-powered descent, NASA employed a system of airbags to cushion the spacecraft's landing. After entering the Martian atmosphere, Pathfinder deployed a parachute, jettisoned its heat shield, and descended safely using this revolutionary airbag cocoon approach.
The landing system lowered the spacecraft from its backshell, using a tether. Then came the tricky part: airbags inflated just eight seconds before landing. Rocket engines on the backshell fired in the moments before landing to smooth the jolt when Pathfinder hit.
Pathfinder then dropped to the surface from a distance of up to 100 feet (30 meters) from the ground, bouncing across the plain for several minutes before rolling safely to a stop.
This was the first time such a system had been used, and NASA was pleased to see that it went so well.
Investigating rocks
Pathfinder's landing spot on Mars was Ares Vallis, an ancient flood plain chosen because it was relatively safe, and also a spot with lots of rocks for Sojourner to analyze.

While Pathfinder was solemnly renamed the Carl Sagan Memorial Station in honor of the recently deceased science popularizer, many of the rocks surrounding Sojourner were given more whimsical names named after cartoon characters.
Sojourner's first stop was analyzing the composition of "Barnacle Bill," a rock just a little ways away from the landing assembly. The two-foot-long rover used an Alpha Proton X-Ray Spectrometer (APSX) to look at the elements inside the rock and found that it had more silica than the surrounding environment.
Silica, an element found in igneous rocks, is a sign of thermal activity. Based on Barnacle Bill's composition, NASA scientists theorized Mars could have had a more interesting geologic history than thought before.
APXS found very different results for some of the other rocks it looked at. "Yogi," for example, appeared to be a basalt, although the results could have been affected by a thin dusting of soil on the rock. "Scooby-Doo" was more sedimentary, similar to the area surrounding it.
What excited scientists the most, though, were the pictures beaming back to Earth showing rounded pebbles and "conglomerate" rocks that indicated something pushing different types of soil together in the past.
NASA said this was evidence of a more water-rich planet, and suggested the plain Sojourner sampled was formed from floods that originated nearby the landing site.
Impact on Mars science
While Sojourner strolled on the surface, Pathfinder was on a mission of its own. It relayed information from the rover to Earth and also took pictures of the Martian sky and surroundings.
On Sol 24, Pathfinder captured a sunset showing a blue color near the sun. The blue is caused by scattering in the dusty Martian atmosphere. It shows up best during sunrise and sunset when the light passes through the densest part of the dust, close to the ground.

Pathfinder also carried magnets on board to measure the magnetic properties of Martian dust. Pictures taken between Sol 10 and Sol 66 showed more dust coating the magnets, which gave scientists a sense of what the dust was made of.
NASA last heard from Pathfinder on Sol 83 of the mission, which in Earth time was Sept. 27, 1997. The agency suspected the cause of the failure was rooted in a dead battery that was affected by repeated charges and decharges.
The lander and rover communicated to Earth nearly three times longer than projected, sending back enough scientific information to keep researchers here busy for years.
Sojourner's APXS experiment was used again on Spirit, Opportunity and Curiosity, each time getting more robust and yielding more data for researchers.
The rover traveled nearly 330 feet (100 meters) during its three months on Mars, never going more than 40 feet (12 m) from the lander. The rover sent more than 550 pictures, and the lander more than 16,500 images.
Many of these pictures went up in nearly real-time on the Pathfinder/Sojourner website, making use of the Internet at a time when interest in the technology exploded among the public. NASA published updates from the mission several times a week.
What's more, the agency still preserves the website in its circa 1997 format, providing a historical time capsule of how early website design was used to talk about space missions.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Elizabeth Howell (she/her), Ph.D., was a staff writer in the spaceflight channel between 2022 and 2024 specializing in Canadian space news. She was contributing writer for Space.com for 10 years from 2012 to 2024. Elizabeth's reporting includes multiple exclusives with the White House, leading world coverage about a lost-and-found space tomato on the International Space Station, witnessing five human spaceflight launches on two continents, flying parabolic, working inside a spacesuit, and participating in a simulated Mars mission. Her latest book, "Why Am I Taller?" (ECW Press, 2022) is co-written with astronaut Dave Williams.