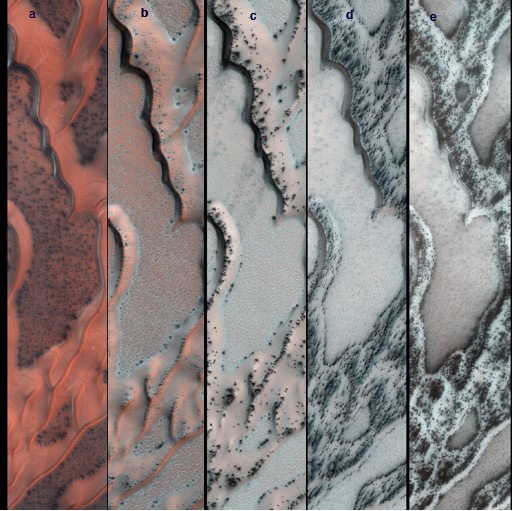
The seasonal thawing of carbon dioxide ice near Mars' north pole carves grooves in the region's sand dunes, three new studies reveal.
The discovery, made using observations from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter spacecraft (MRO), reinforces that the Red Planet's surface continues to be transformed today, even though Mars' volcanoes have died out and its liquid surface water apparently dried up long ago.
"It's an amazingly dynamic process," Candice Hansen of the Planetary Science Institute in Tucson, Ariz., lead author of one of the studies, said in a statement. "We had this old paradigm that all the action on Mars was billions of years ago. Thanks to the ability to monitor changes with the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, one of the new paradigms is that Mars has many active processes today."
MRO photographed dunes in Mars' far northern latitudes using its High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment camera, or HiRise. The images revealed a number of grooves appearing in the dunes as the northern spring took hold and progressed. [Dry Ice 'Smoke' Moves Mars Sand (Video)]
The phenomenon is driven by the springtime thawing of a surface layer of frozen carbon dioxide, also known as dry ice.
This thawing occurs first on the ice layer's underside, which is in contact with the warming ground, researchers said. The dry ice sublimes from a solid state to a gaseous one, and pressure builds as more and more gas is produced and trapped.
Eventually, cracks form in the ice and some of the carbon dioxide gas breaks free, forming temporary grooves in the dune as it hisses out.
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
The escaping gas also carries sand, which forms dark streaks as it spills across the dry ice covering the dune. These dark fans disappear as the seasonal ice evaporates, and Martian winds erase most of the newly formed grooves before the next winter and springtime roll around.
The grooves are smaller versions of the "gullies" MRO has spotted on other, steeper Martian dunes, which were apparently formed in a similar way, researchers said. And similar processes have been observed near the Red Planet's south pole.
"It is a challenge to catch when and how those changes happen, they are so fast," Ganna Portyankina of the University of Bern in Switzerland, lead author of another one of the studies, said in a statement. "That's why only now we start to see the bigger picture that both hemispheres actually tell us similar stories."
The three new studies, which appear in the journal Icarus, were based on observations made by MRO over three Martian years, or about six Earth years. The papers document a variety of seasonal changes on Mars, including the dune grooves and the distribution of water frost, which is blown around by springtime winds.
Follow SPACE.com senior writer Mike Wall on Twitter @michaeldwall or SPACE.com @Spacedotcom. We're also on Facebook and Google+.

Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.

Michael Wall is a Senior Space Writer with Space.com and joined the team in 2010. He primarily covers exoplanets, spaceflight and military space, but has been known to dabble in the space art beat. His book about the search for alien life, "Out There," was published on Nov. 13, 2018. Before becoming a science writer, Michael worked as a herpetologist and wildlife biologist. He has a Ph.D. in evolutionary biology from the University of Sydney, Australia, a bachelor's degree from the University of Arizona, and a graduate certificate in science writing from the University of California, Santa Cruz. To find out what his latest project is, you can follow Michael on Twitter.