Antikythera Anniversary: Astronomical Computer Still Puzzles After 115 Years
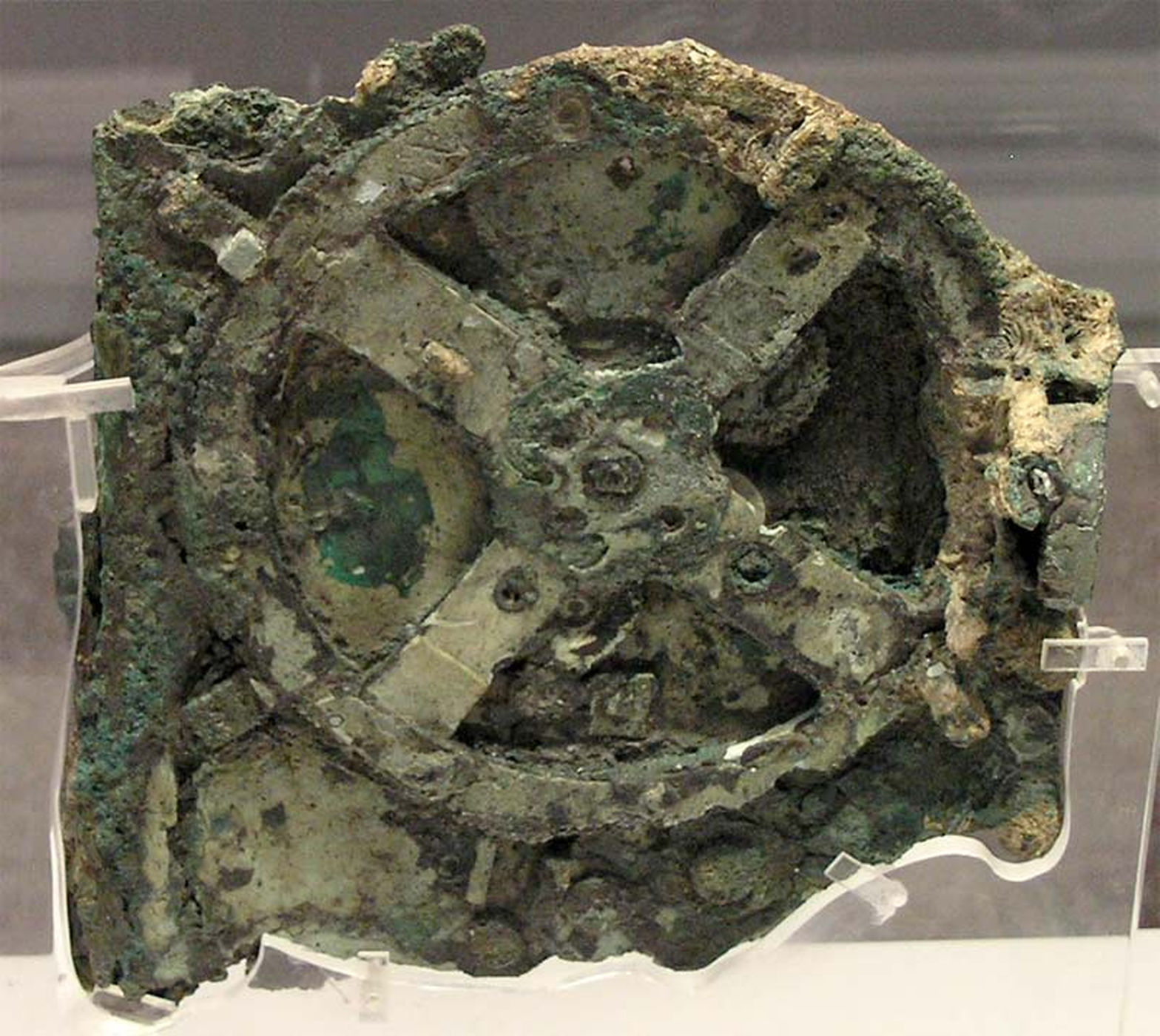
What looked like a hunk of corroded metal lying at the bottom of the Aegean Sea near the Greek island of Antikythera turned out to be a piece of a mysterious astronomical calculator. That was 115 years ago, on May 17, 1902, when archaeologist Valerios Stais discovered the bronze bit among other artifacts discovered on the Roman cargo ship called the Antikythera shipwreck.
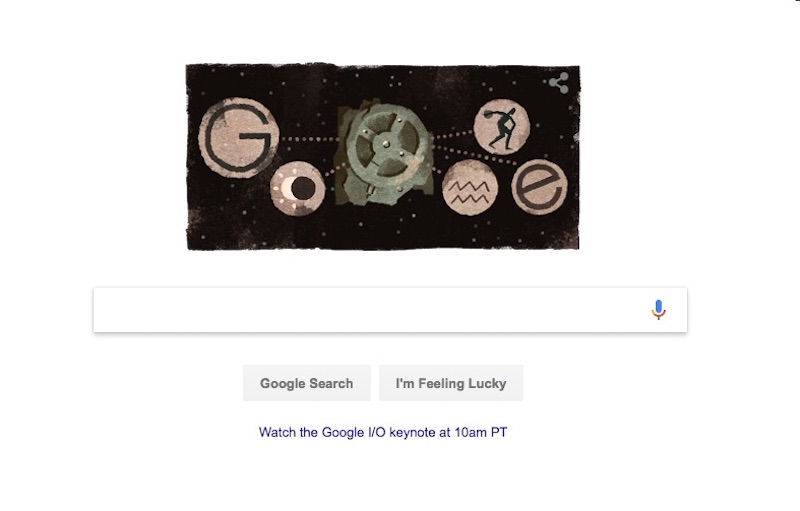
Today's Google Doodle celebrates that discovery with an illustration showing the biggest part of the Antikythera mechanism, which looks like a gear or wheel. Dating to about 85 B.C., or even earlier, the shoebox-size computer is intricate, with dials on the outside and 30 bronze gear wheels inside. Long ago, Greeks could have turned a hand crank on the device to reveal everything from the positions of the sun and the moon and the lunar phases to the cycles of the Greek Olympics. [Photos: Ancient Greek Shipwreck Yields Antikythera Mechanism]
The Antikythera mechanism was also equipped with a dial to predict eclipses. (The Google Doodle includes illustrations for some of these uses, such as the Olympic Games.)
To this day, historians and scientists continue to study the 2,000-year-old computer to reveal more of its secrets. For instance, scientists reported last summer that they found a user's guide of sorts hidden in text on the 82 corroded metal fragments that make up the Antikythera mechanism. Much of the Greek text is unreadable to the naked eye, but with new imaging methods, such as 3D X-ray scanning, scientists have been able to view the once-hidden letters and words.

"Before, we could make out isolated words, but there was a lot of noise —letters that were being misread or gaps in the text," Alexander Jones, a professor of the history of science at New York University, told Live Science last year. "Now, we have something that you can actually read as ancient Greek. We can tell what these texts were saying to an ancient observer."
Jones and colleagues found that those inscriptions on the front and back of the mechanism would have been a key for all of the dials and what they were used for.
"That's where we get the key information that there was a full-blown display of planets moving through the zodiac on the front," Jones said last year. This display, which is now lost, had pointers with small spheres representing the sun, moon and planets known at the time (Mars, Jupiter and Saturn) arranged in a geocentric system with circular orbits around Earth, according to the inscription on the back cover. Researchers had proposed the existence of this feature before, but they never had any physical evidence for it, Jones said.
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
Also last year, archaeologists discovered the 2,000-year-old skeleton of a young man found on the Antikythera shipwreck. The skeleton could divulge the first DNA evidence from the famed wreck, researchers said.
Original article on Live Science.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.


