See a lunar scar darken the crescent moon tonight
Lunar maria or 'seas' formed when lava flooded impact basins billions of years ago.
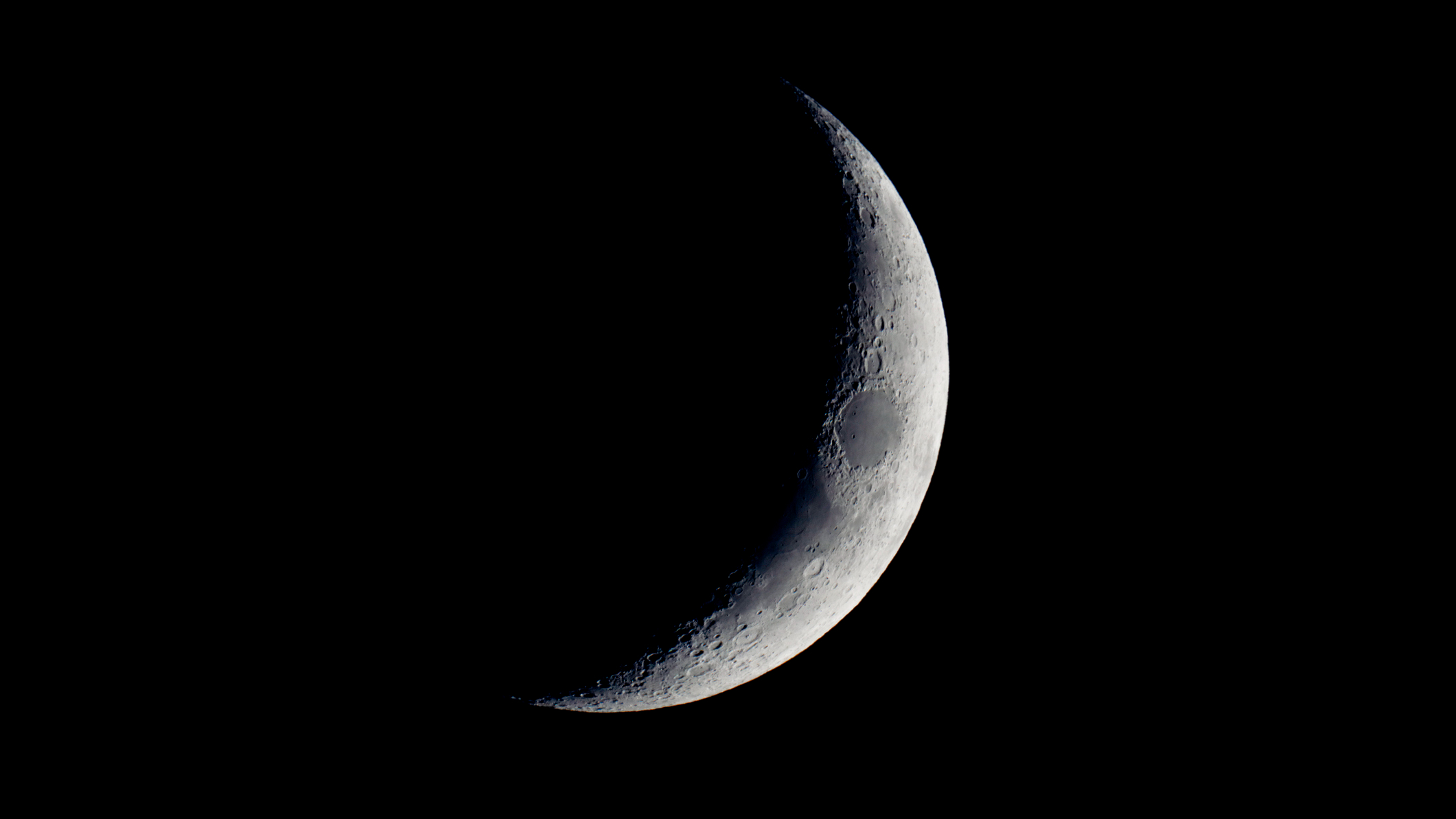

May 30 presents a perfect opportunity to spot Mare Crisium — a dark Nevada-sized patch — etched into the delicate curve of the crescent moon before it sinks below the horizon around midnight.
Skywatchers in the U.S. will find the moon's sickle-like form hanging around 30 degrees above the western horizon after sunset on May 30, with around 16% of its surface illuminated by direct sunlight, according to stargazing website in-the-sky.org. On May 30, the moon is in the constellation Cancer, with the Beehive cluster close to its left and Mars shining just beyond. To the right, the bright stars Castor and Pollux also make an appearance.
The moon is among the most popular targets for astronomers, thanks to the ever-shifting play of light and shadow across its surface. As it makes its near month-long journey around Earth, a myriad of different regions and features come into stark relief, changing night by night. And yet, for all this variety, the moon only ever shows a single side to us as it's tidally locked to our planet.
One such feature is the dark lunar maria (Latin for 'seas'), formed when molten lava flooded a network of impact basins that scarred the moon's surface billions of years ago. These lava flows swiftly cooled in the frigid environment of space, leaving behind vast basaltic plains that remain easily visible to the naked eye today.
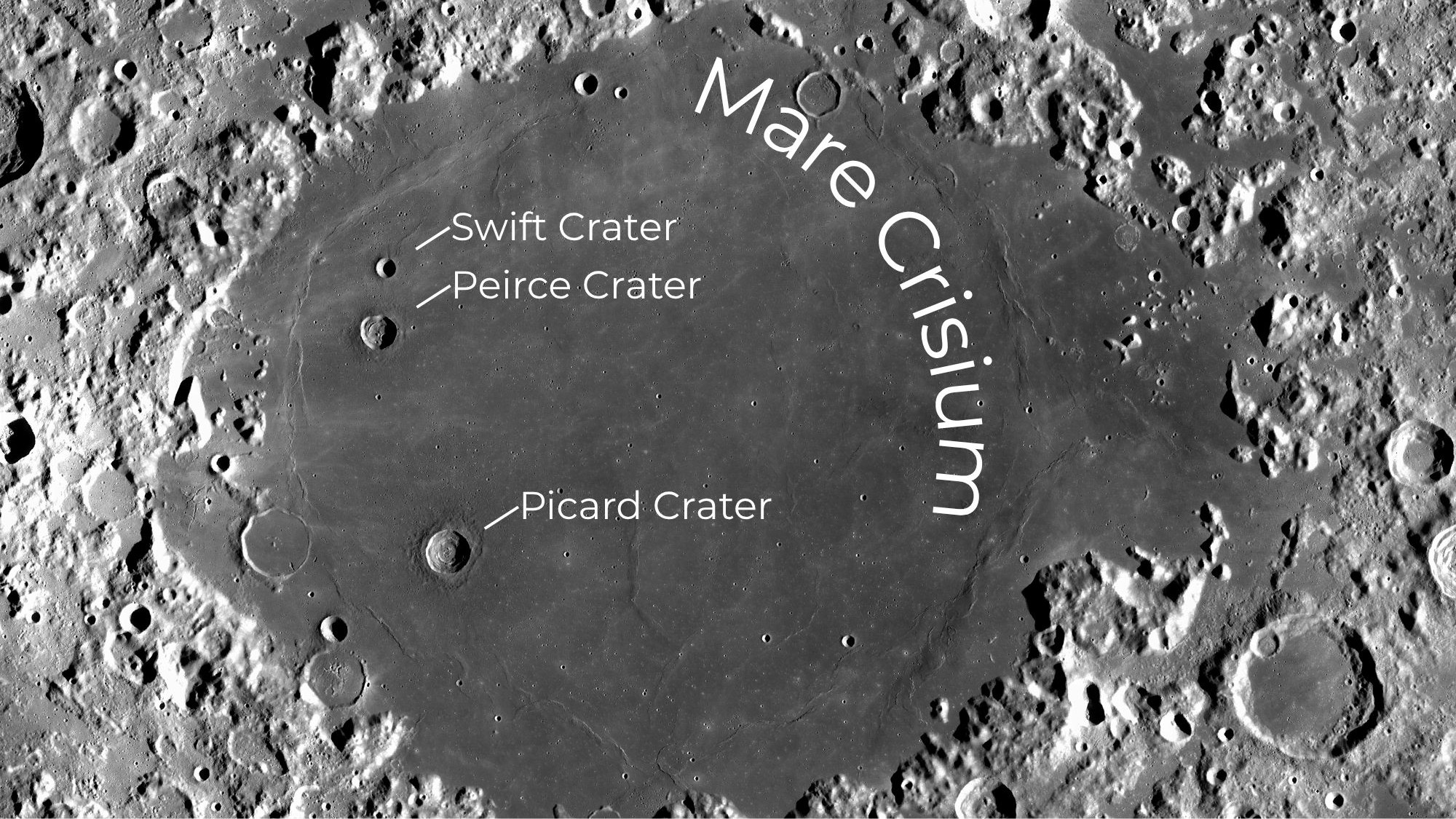
Mare Crisium, or the 'Sea of Crises', can be spotted on the night of May 30 as an oval-shaped dark patch on the moon's northeastern limb, close to the terminator — the line that separates day from night on any solar system body.
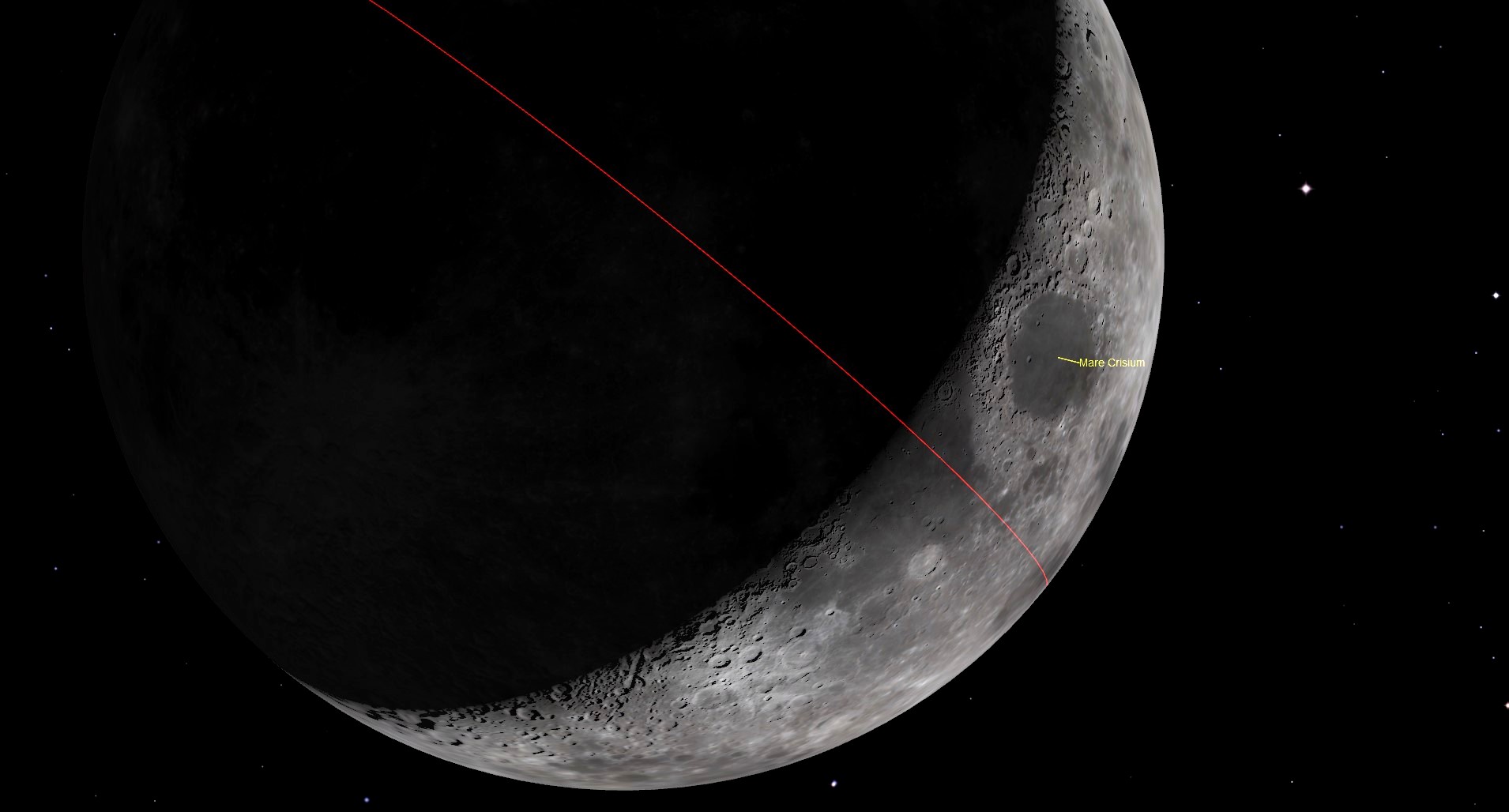

Spanning 345 miles (555 kilometers), this lunar mare is visible to the naked eye, though a pair of 10x50 binoculars will reveal more of the craggy region surrounding the lunar sea. An entry-level 6-inch telescope, meanwhile, will allow you to pick out the 14-mile-wide (23 km) Picard Crater that stands alone near the south-western rim of the Nevada-sized plane, according to NASA. Just above Picard lies the similarly sized Peirce Crater, with the smaller Swift Crater just beyond.
Before the moon dips below the western horizon around midnight local time, moongazers may also catch sight of its shadowed expanse faintly glowing — an effect known as earthshine, caused by sunlight reflected off Earth softly illuminating the moon's night side.
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Want to explore the lunar surface for yourself? The Celestron NexStar 4SE is ideal for beginners wanting quality, reliable and quick views of celestial objects. For a more in-depth look at our Celestron NexStar 4SE review.
The closest humans have come to Mare Crisium was during the final moon mission of the Apollo era, when Apollo 17 astronauts Eugene Cernan, Ron Evans and Harrison "Jack" Schmitt landed on the eastern edge of Mare Serenitatis. However, Mare Crisium did serve as the landing site of the Soviet Luna 15 and Luna 24 robotic missions, and it made headlines again in March 2025 with the successful touchdown of Firefly Aerospace's Blue Ghost lander.
Anyone interested in exploring the lunar surface for themselves should check out our guides to the best binocular and telescope deals available in 2025. Also, be sure to read up on our guide to photographing and exploring the moon's surface.
Editor's Note: If you would like to share your astrophotography with Space.com's readers, then please send your photo(s), comments, and your name and location to spacephotos@space.com.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.

Anthony Wood joined Space.com in April 2025 after contributing articles to outlets including IGN, New Atlas and Gizmodo. He has a passion for the night sky, science, Hideo Kojima, and human space exploration, and can’t wait for the day when astronauts once again set foot on the moon.
You must confirm your public display name before commenting
Please logout and then login again, you will then be prompted to enter your display name.
