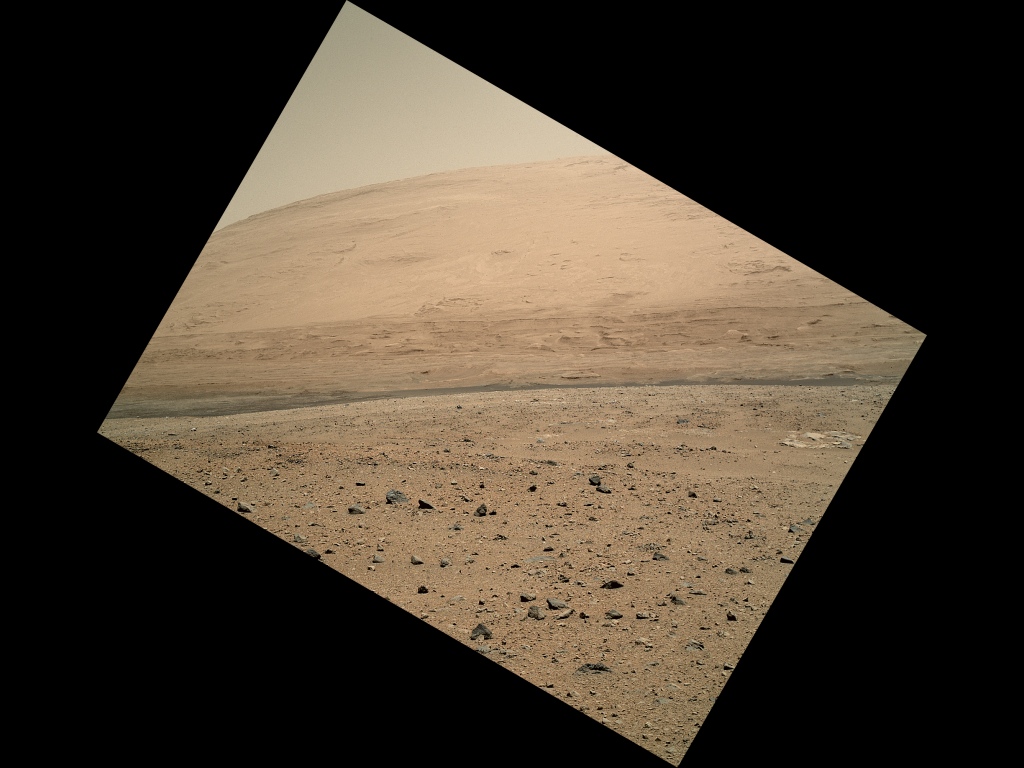
NASA's Mars rover Curiosity is really starting to stretch its legs on the Red Planet.
The 1-ton Curiosity rover made by far the longest drive of its nearly year-long surface mission on Sunday (July 21), traversing 329 feet (100.3 meters) of Martian terrain. The robot's one-day distance record prior to Sunday had been 161 feet (49 m), NASA officials said.
Good views of Curiosity's surroundings allowed the rover to cover so much ground on Sunday, the 340th Martian day, or sol, of its Red Planet mission. [Curiosity's Latest Amazing Mars Photos]
"What enabled us to drive so far on Sol 340 was starting at a high point and also having Mastcam images giving us the size of rocks so we could be sure they were not hazards," rover planner Paolo Bellutta, of NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif., said in a statement, referring to Curiosity's head-mounted camera system.
"We could see for quite a distance, but there was an area straight ahead that was not clearly visible, so we had to find a path around that area," Bellutta added.
While Bellutta and his colleagues guided Sunday's drive, mission team members plan to start using the rover's autonomous navigation capability soon. Long treks may thus become more and more common for Curiosity in the coming weeks, officials said.
The car-size rover is three weeks into an epic journey to a huge and mysterious mountain called Mount Sharp, which rises 3.4 miles (5.5 kilometers) into the Red Planet sky. The team is targeting a spot near Mount Sharp's base that lies nearly 5 miles (8 km) from Curiosity's current location.
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
Mission scientists want Curiosity to climb up through Mount Sharp's foothills, reading the history of Mars' changing environmental conditions as it goes.
Rover team members have said the drive to Mount Sharp may take a year or so. There is no set timeline, however, as mission scientists want the freedom to check out interesting features and formations along the way.
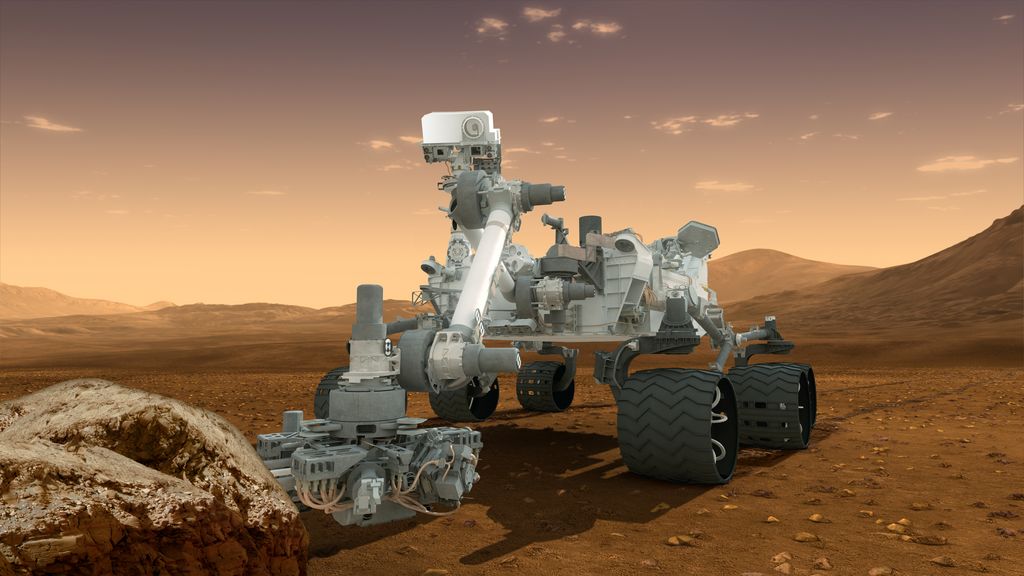
Curiosity touched down on Aug. 5, 2012, kicking off a planned two-year surface mission to determine if Mars could ever have supported microbial life. The rover has already checked off this goal, finding that an area near its landing site was indeed habitable billions of years ago.
The rover's odometery stands at 0.81 miles (1.23 km) as of today (July 23), NASA officials said. Curiosity's top speed over flat, hard ground is about 0.09 mph (0.14 km/h).
Follow Mike Wall on Twitter @michaeldwall and Google+. Follow us @Spacedotcom, Facebook or Google+. Originally published on SPACE.com.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.

Michael Wall is a Senior Space Writer with Space.com and joined the team in 2010. He primarily covers exoplanets, spaceflight and military space, but has been known to dabble in the space art beat. His book about the search for alien life, "Out There," was published on Nov. 13, 2018. Before becoming a science writer, Michael worked as a herpetologist and wildlife biologist. He has a Ph.D. in evolutionary biology from the University of Sydney, Australia, a bachelor's degree from the University of Arizona, and a graduate certificate in science writing from the University of California, Santa Cruz. To find out what his latest project is, you can follow Michael on Twitter.