90 Years Ago, the Liquid-Fueled Rocket Changed Space Travel Forever
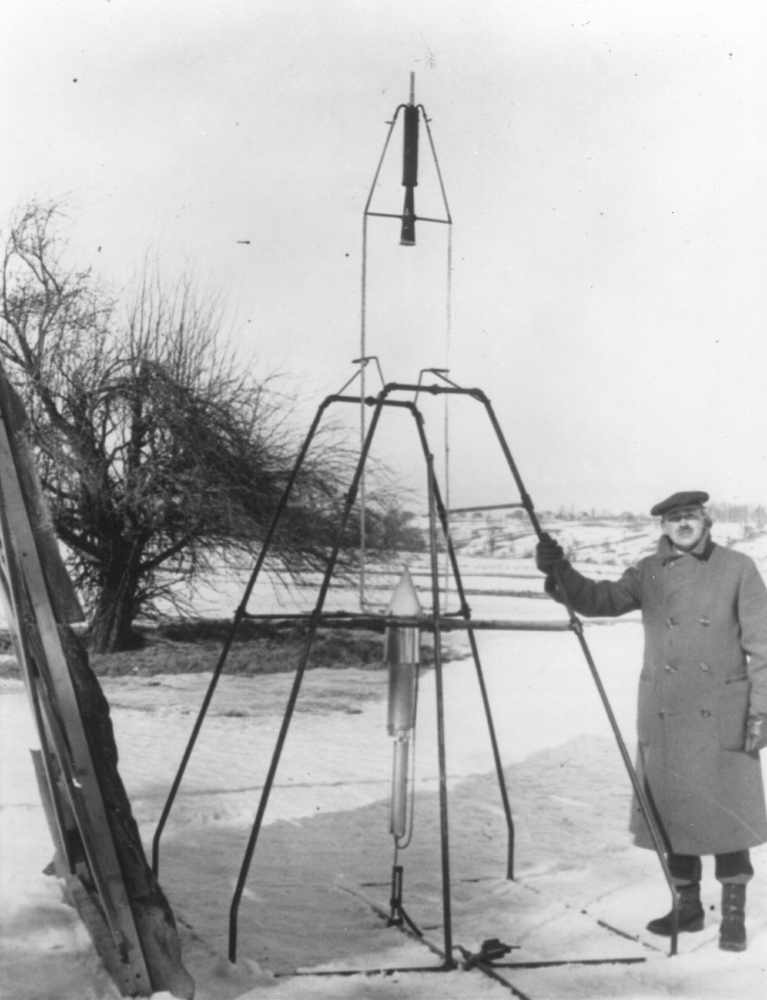

Launches of liquid-fueled rockets may be relatively routine today, but 90 years ago, they were brand-new. In fact, the first liquid-fueled rocket launched on March 16, 1926, under the direction of rocketry pioneer Robert Goddard.
A newly re-released animation (shown here) shows NASA employees celebrating the launch of Goddard's small rocket during a 1976 celebration (which was the 50th anniversary of the historic test flight).
The looped animation shows employees gathered in front of a school bus at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, which was named in honor of Robert Goddard, watching the rocket replica take off. Liquid propellant is used for most major space launches today, from human flights to interplanetary missions.
Goddard's first liquid-fueled rocket was small and did not fly all that high, but it marked a big change in how rocketry is done. Previously, all rocket launches had been done with solid materials. That work dated back to the 13th century, when Chinese engineers used gunpowder when repelling enemies.
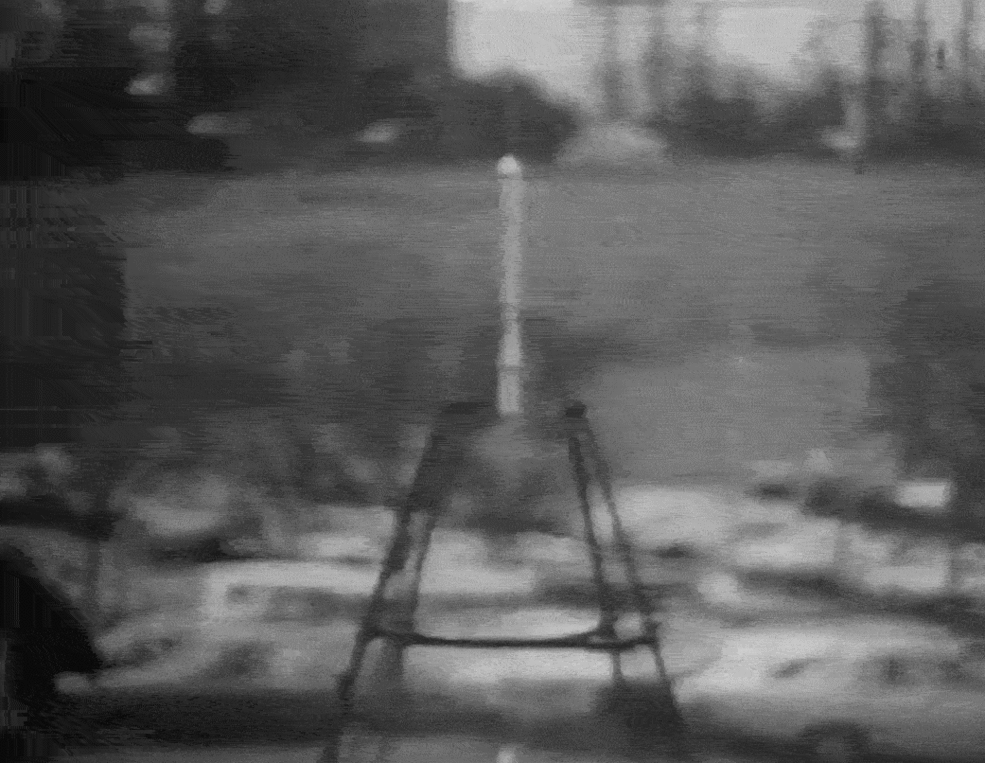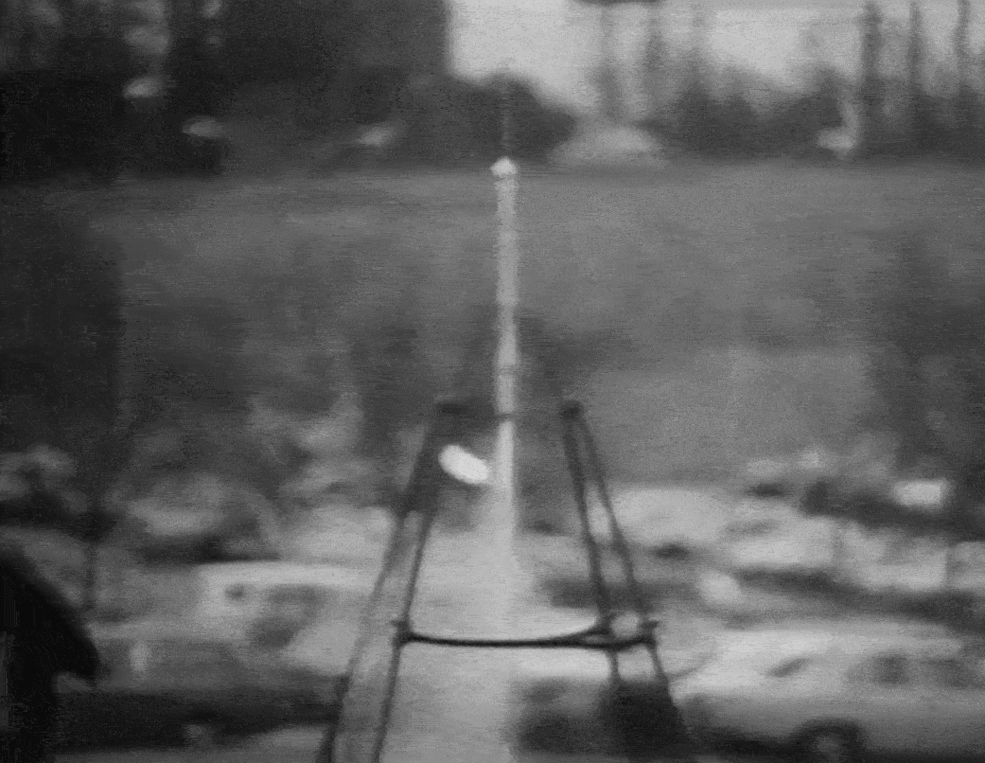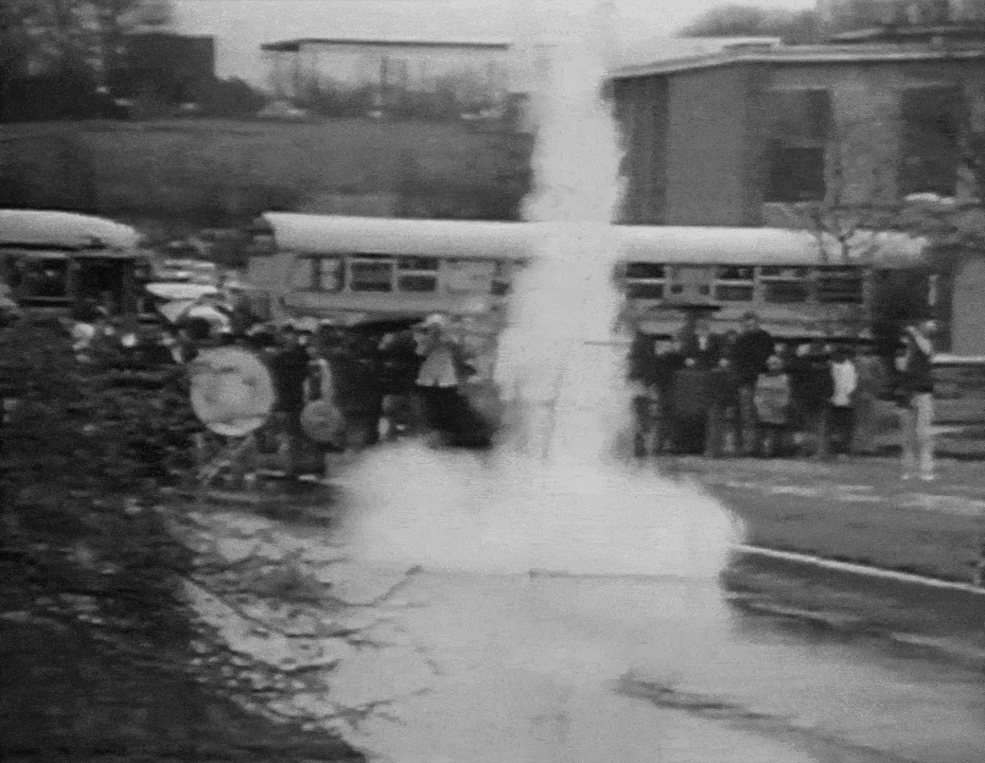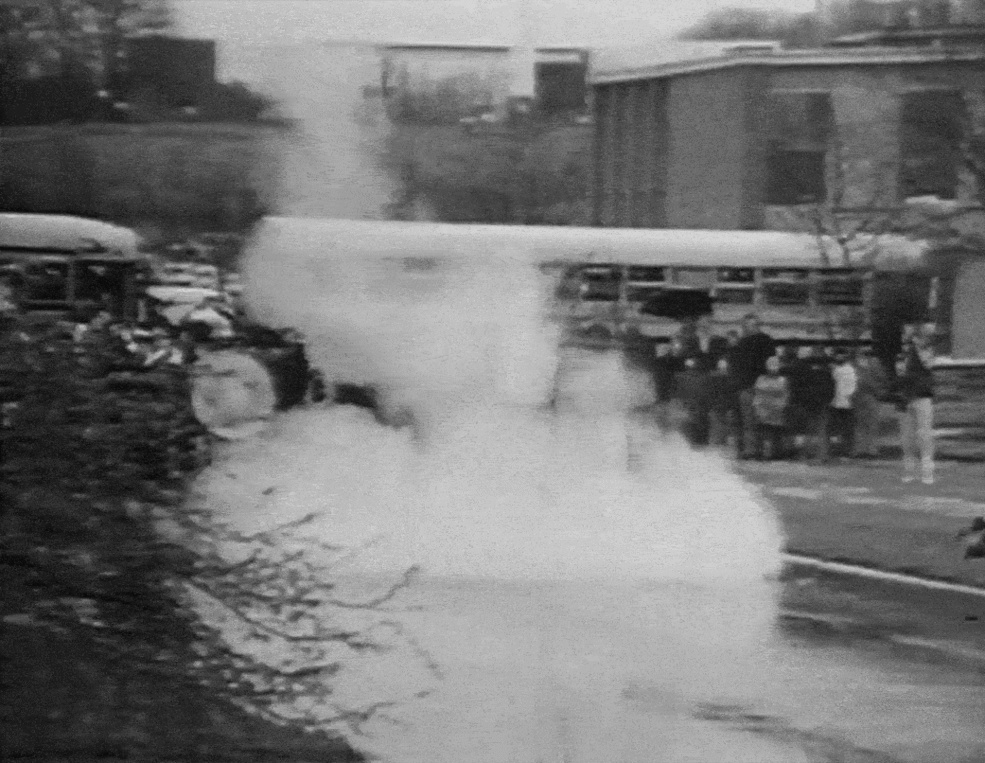
Goddard, however, believed that liquid would offer more advantages than solid materials. Liquid rockets provide more thrust per unit of fuel and allow engineers to specify how long the rocket will stay lit.
It took 17 years of work for Goddard's first launch to fly.
"It looked almost magical as it rose, without any appreciably greater noise or flame, as if it said, 'I've been here long enough; I think I'll be going somewhere else, if you don't mind,'" Goddard wrote in his journal the next day, according to a NASA statement.
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
Goddard dreamed of seeing interplanetary travel made possible. It didn't happen while he was still alive — he died in 1945 — but liquid rocketry became very important in space history.
The first satellite, Sputnik, was launched in 1957 using a rocket that in part used liquid fuel. Liquid fuel was also used for the massive Saturn V rocket that took astronauts to the moon in the 1960s and 1970s. Liquid remains the fuel type of choice for human missions to this day; because the burn can be controlled, it is safer than solid rocket propellants.
Other rockets with liquid fuels in one or more stages include the European Ariane 5 (which will launch NASA's James Webb Space Telescope), Russia's Soyuz boosters, United Launch Alliance's Atlas V and Delta booster family, and SpaceX's Falcon 9 rocket, among many others.
In his lifetime and after his death, Goddard received more than 200 patents for his inventions. One of his major works included inventing multistage rockets, which are a foundation for just about every spaceflight today. They allow a rocket to have multiple fuel tanks and engines, which are discarded as the rocket gets higher in the atmosphere.
"The U.S. failed to recognize the full potential of his [Goddard's] work until after his death — in fact, some of his ideas about reaching outer space were ridiculed during his lifetime," NASA wrote in the same statement. "But the first liquid-fueled rocket flight was as significant to space exploration as the Wright brothers' first flight was to air travel, and 90 years later, his patents are still integral to spaceflight technology."
Follow Elizabeth Howell @howellspace, or Space.com @Spacedotcom. We're also on Facebook and Google+. Original article on Space.com.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.

Elizabeth Howell (she/her), Ph.D., was a staff writer in the spaceflight channel between 2022 and 2024 specializing in Canadian space news. She was contributing writer for Space.com for 10 years from 2012 to 2024. Elizabeth's reporting includes multiple exclusives with the White House, leading world coverage about a lost-and-found space tomato on the International Space Station, witnessing five human spaceflight launches on two continents, flying parabolic, working inside a spacesuit, and participating in a simulated Mars mission. Her latest book, "Why Am I Taller?" (ECW Press, 2022) is co-written with astronaut Dave Williams.
