Carina Nebula: Amazing Photos of a Colorful Cosmic Cloud
Pillars of Destruction
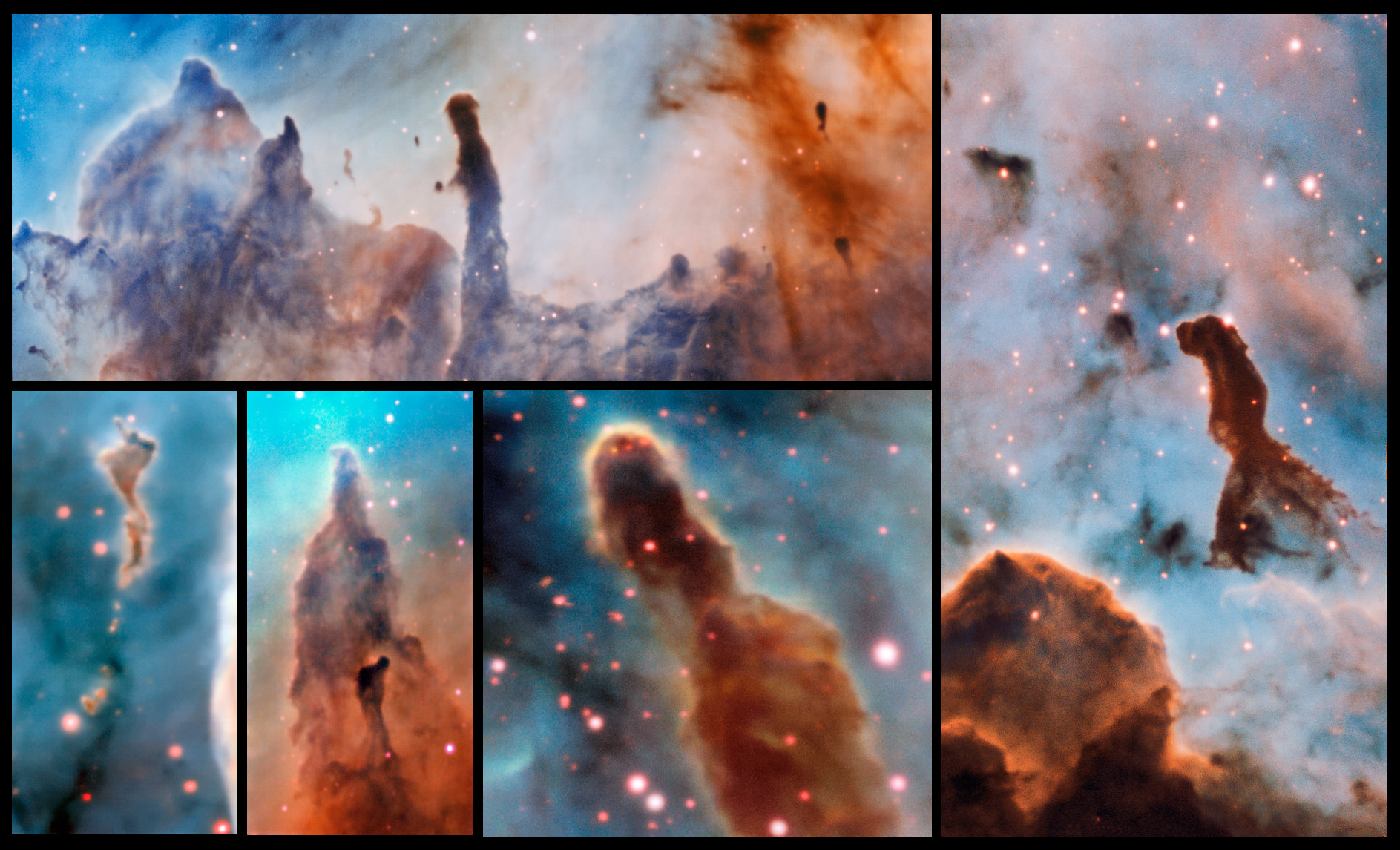

The Carina Nebula (NGC 3372) is a stellar nursery 7,500 light-years from Earth. These images show several pillars of gas and dust protruding from the nebula. Dubbed the "Pillars of Destruction," these regions are being destroyed by radiation from new stars. The European Southern Observatory's Very Large Telescope in Chile created these images with the Multi Unit Spectroscopic Explorer (MUSE) instrument.
Region R18 in the Carina Nebula
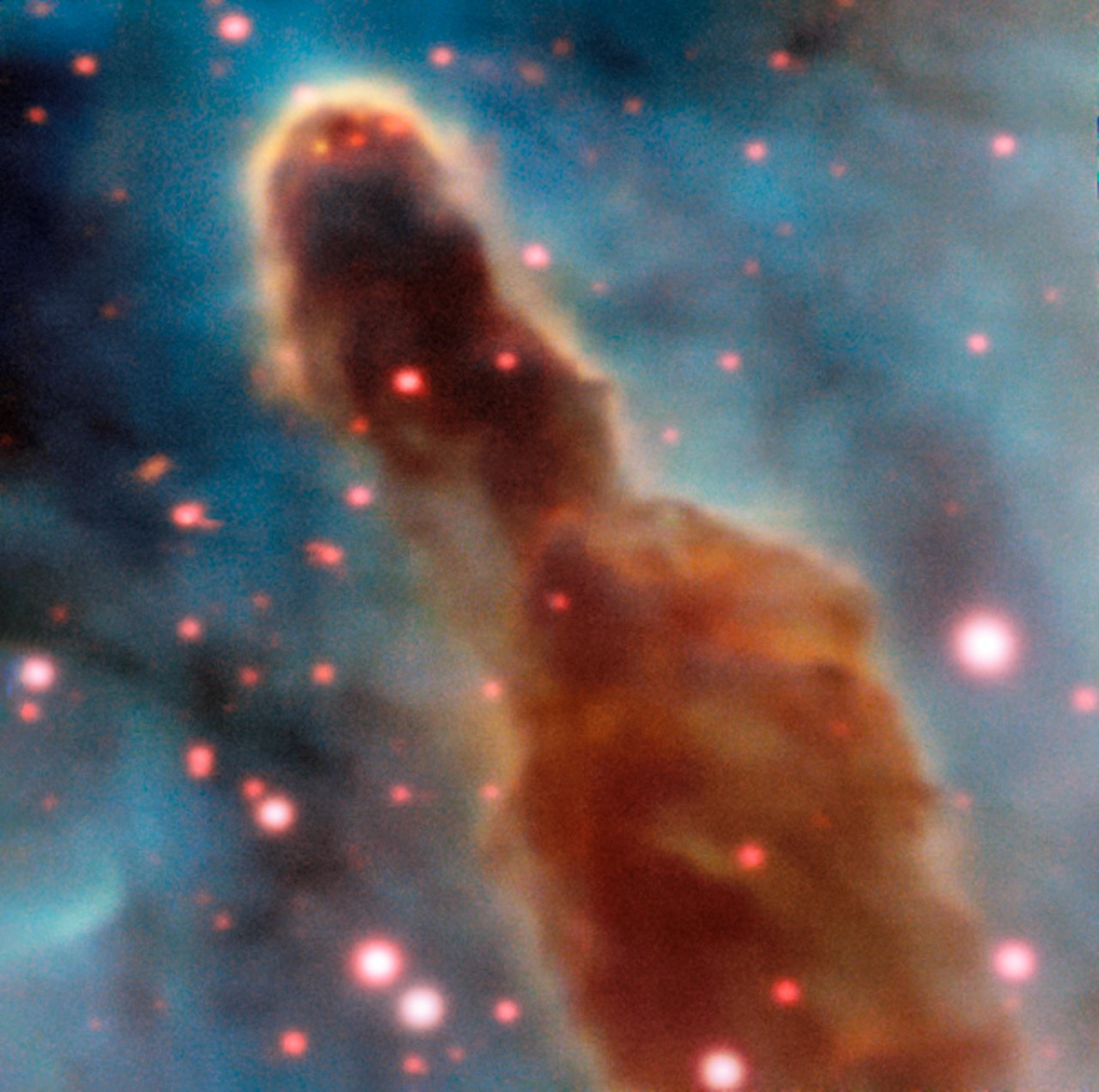

The MUSE instrument on ESO's Very Large Telescope captured the R18 region inside the Carina Nebula. The pillars of dust and gas which produce gigantic stars are eventually consumed by the stars themselves.
Region R37 in the Carina Nebula
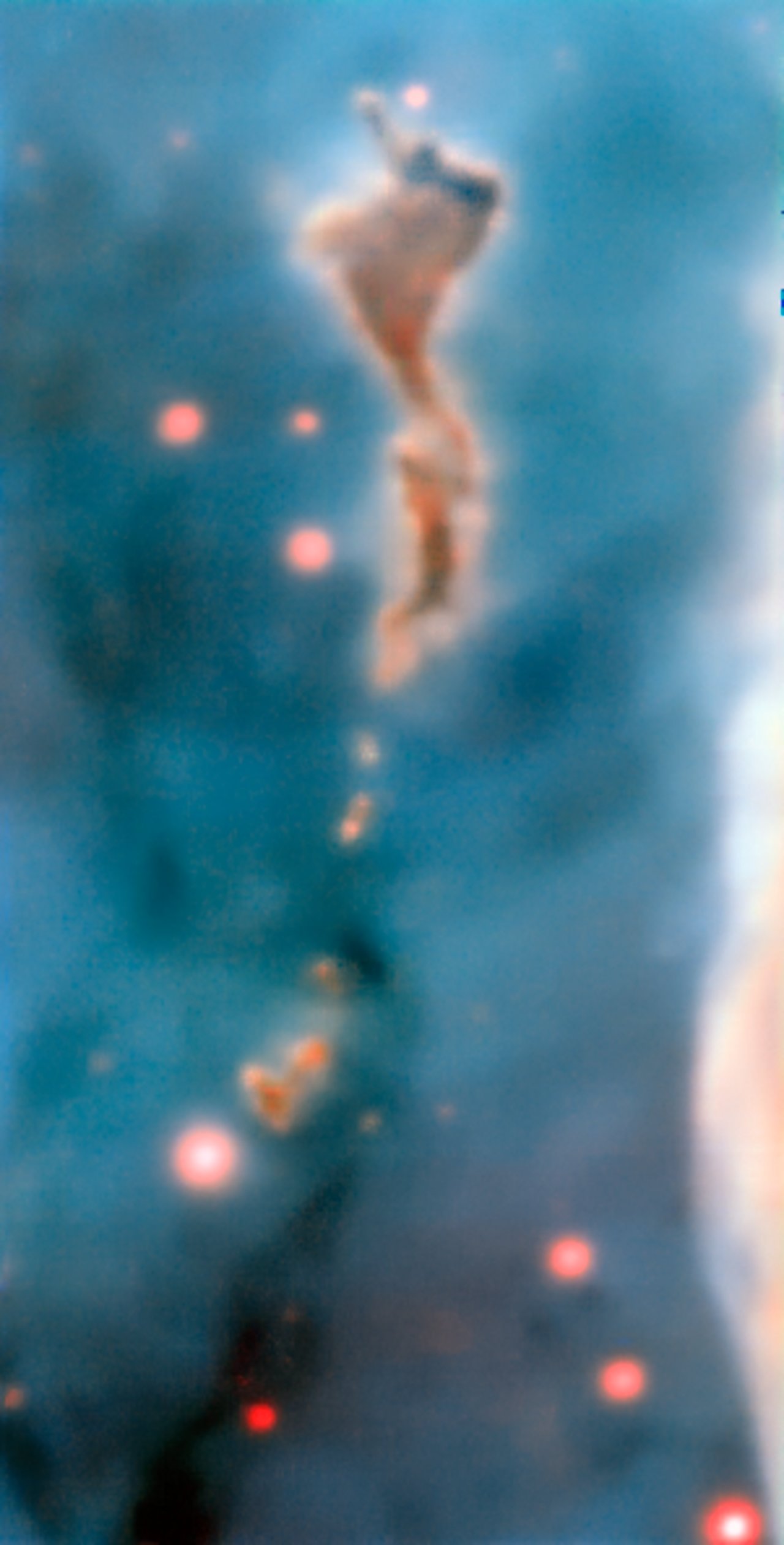
Massive newborn stars inside the Carina Nebula's R37 region, which is 7500 light-years away, destroy the clouds of dust and gas that created them. This image was taken by the MUSE instrument on ESO’s Very Large Telescope.
Region R45 in the Carina Nebula
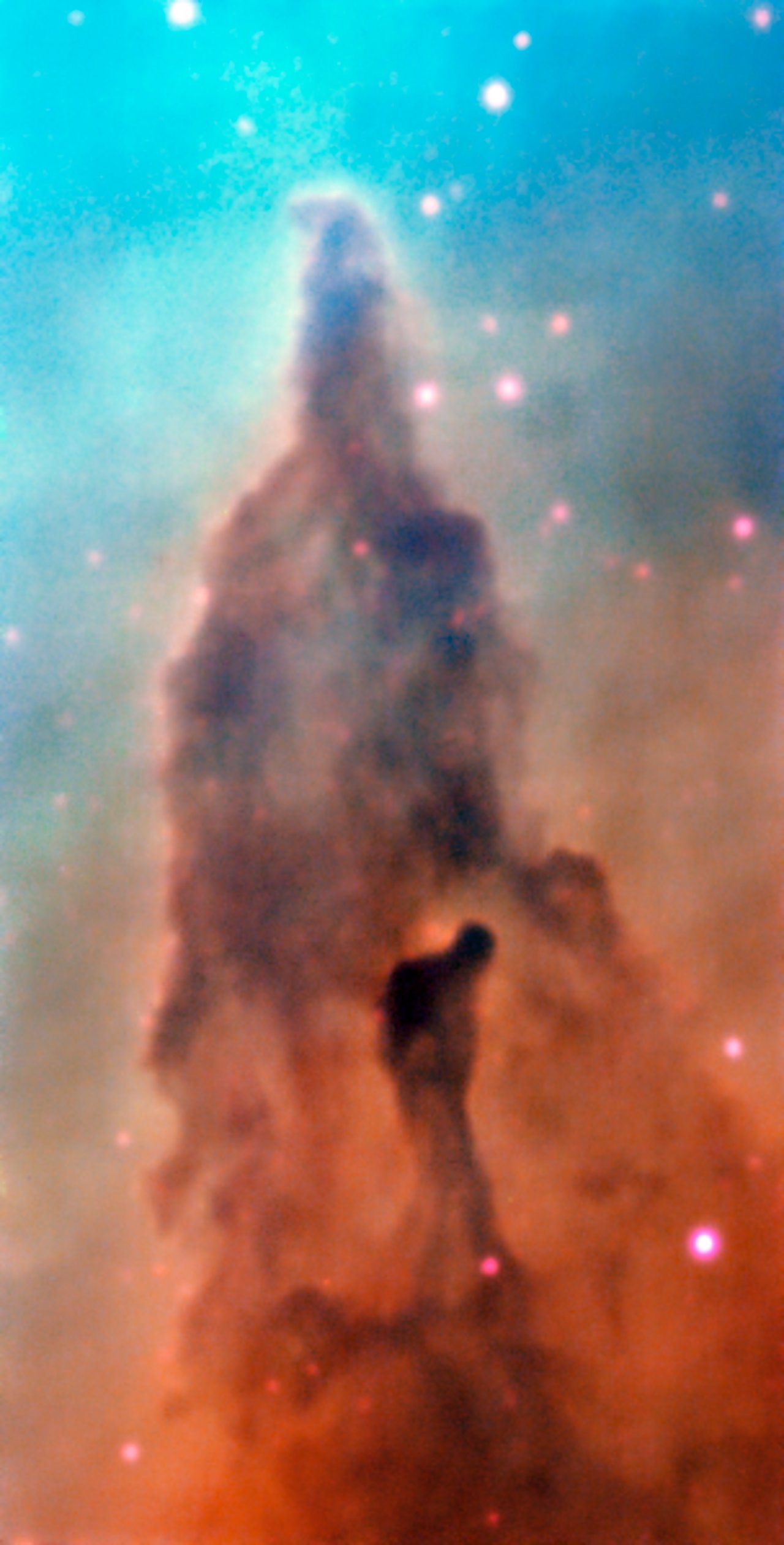

In the R45 Region of the Carina Nebula, the massive stars that spawn from the cosmic gas and dust slowly devour the clouds that birthed them.
Star Cluster Trumpler 14
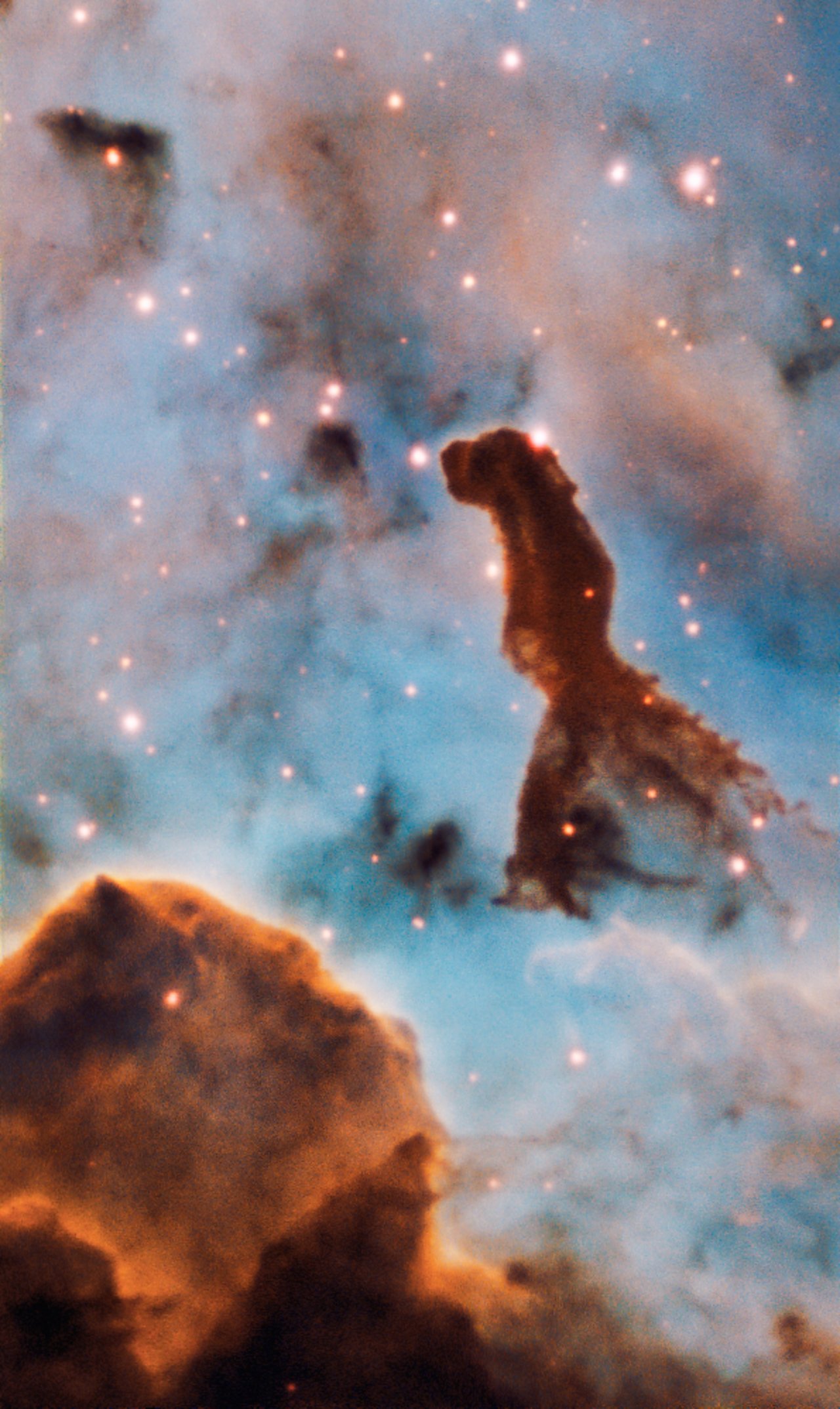

Inside the Carina Nebula, this pillar from the Trumpler 14 star cluster was captured by the MUSE instrument on the ESO's Very Large Telescope.
R44 Region in the Carina Nebula
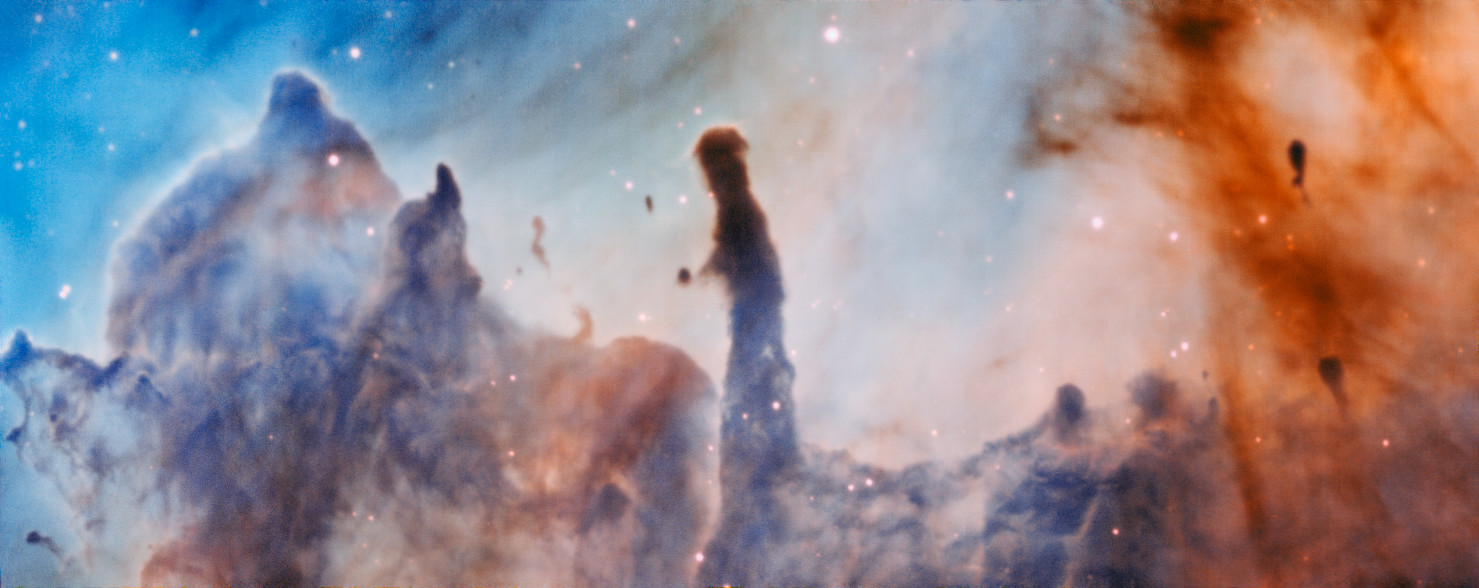

This photo shows a region of the Carina Nebula (NGC 3372) called R44. The European Southern Observatory's Very Large Telescope in Chile created the image with the Multi Unit Spectroscopic Explorer (MUSE) instrument.
Mystic Mountain
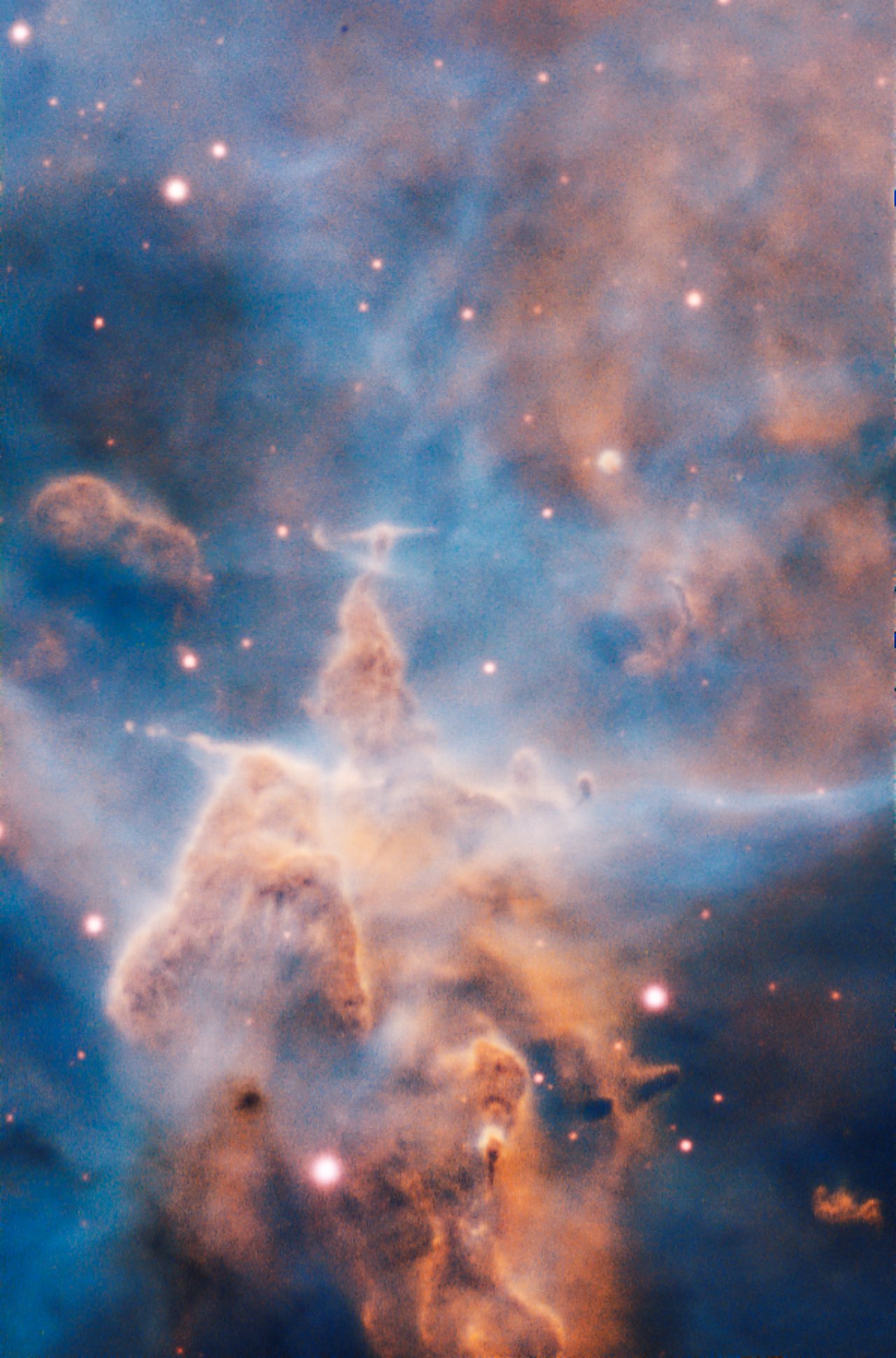

This majestic pillar of the Carina Nebula (NGC 3372) is a 3-light-year-tall cloud of gas and dust that is being eaten away by the brilliant light from stars both in its surroundings and inside the cloud itself. The European Southern Observatory's Very Large Telescope in Chile created the image with the Multi Unit Spectroscopic Explorer (MUSE) instrument.
Bok Globules
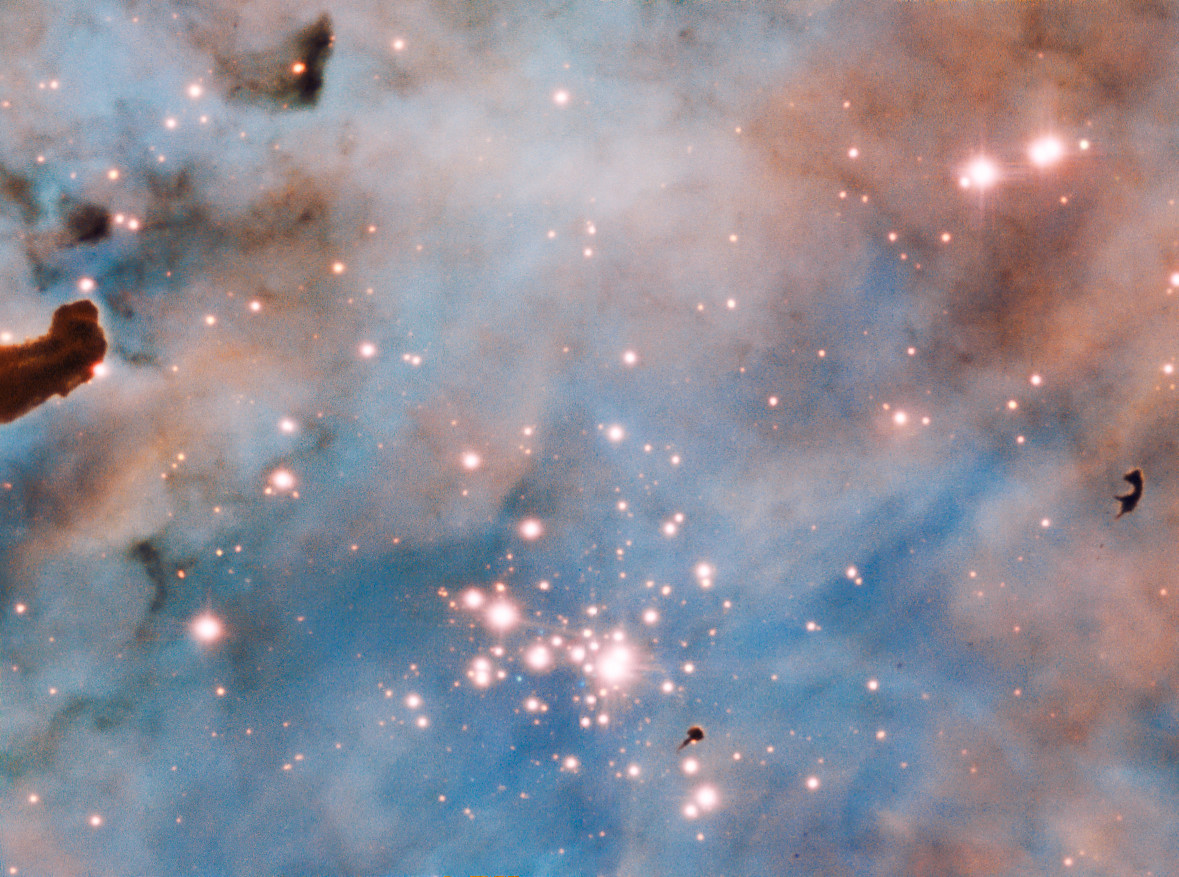

Dark patches seen in this region of the Carina Nebula (NGC 3372) are called "Bok globules." These small, dark nebulas are dense with gas and dust, so not much light can get through. The European Southern Observatory's Very Large Telescope in Chile created this image with the Multi Unit Spectroscopic Explorer (MUSE) instrument.
Violent Carina Nebula Seen in Detail
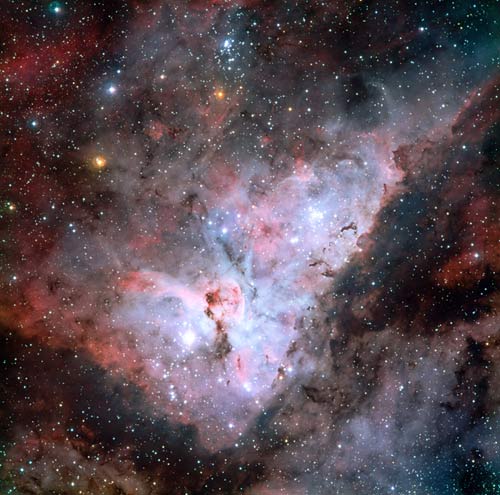

Several well known astronomical objects in and near the Carina Nebula can be seen in this wide field image: to the bottom left of the image is one of the most impressive binary stars in the Universe, Eta Carinae, with the famous Keyhole Nebula just adjacent to the star. The collection of very bright, young stars above and to the right of Eta Carinae is the open star cluster Trumpler 14. A second open star cluster, Collinder 228 is also seen in the image, just below Eta Carinae. North is up and East is to the left.
Eta Carina Nebula
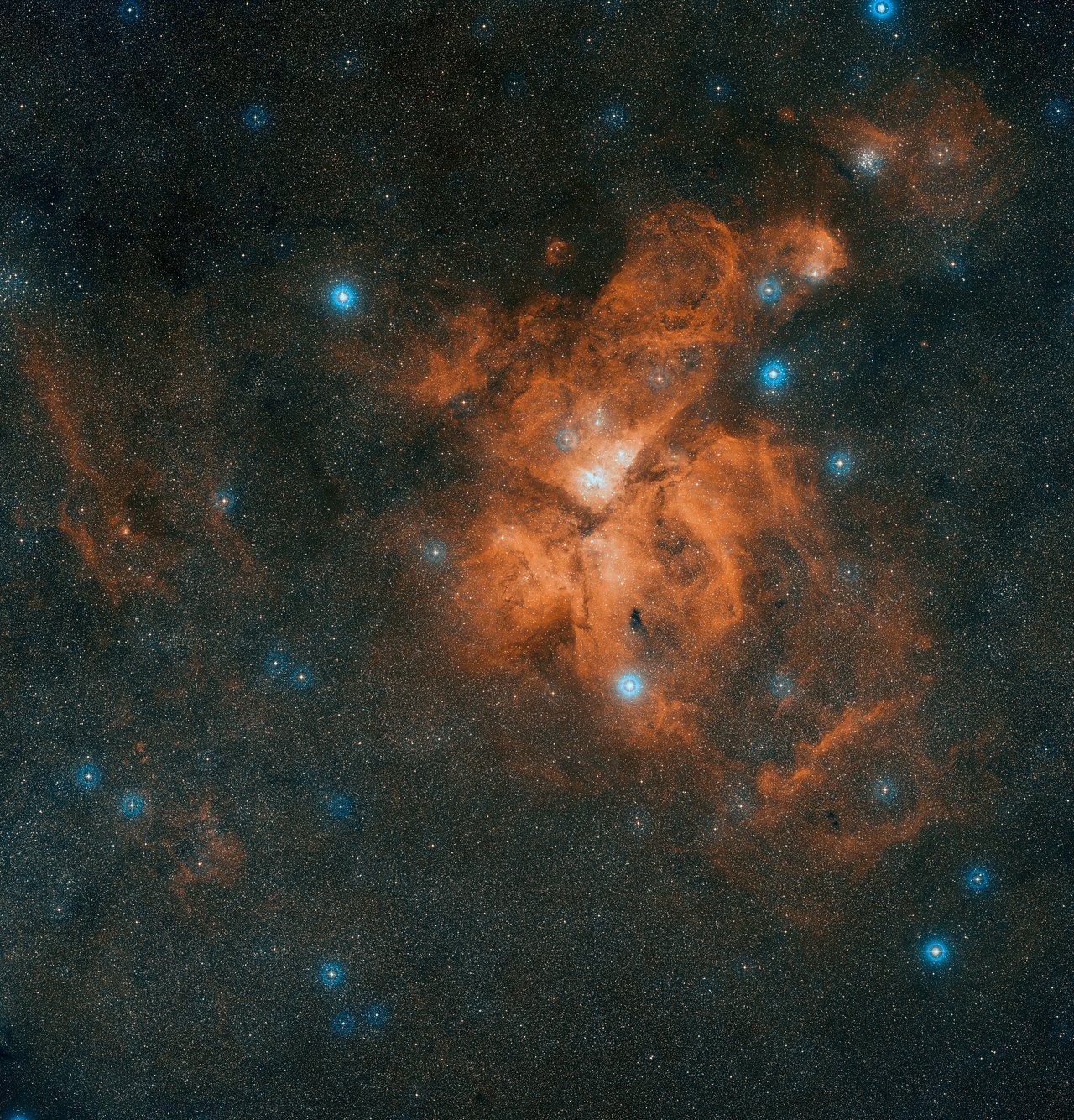

The Digitized Sky Survey 2 created this color composite of the Eta Carina Nebula from multiple exposures.
Carina Nebula Over ALMA
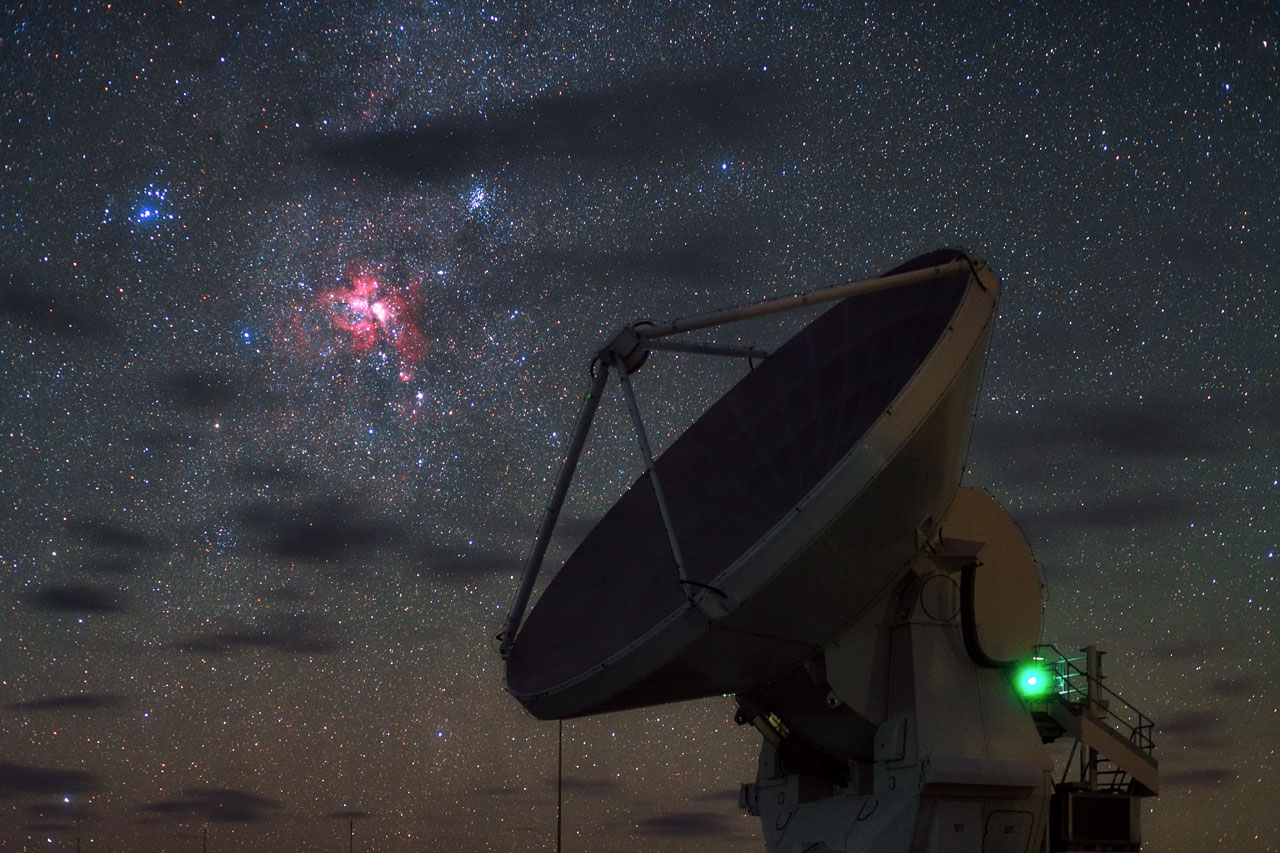

The Carina Nebula glows over the ALMA telescope on the Chajnantor plateau in the Chilean Andes. Image released Nov. 30, 2015.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Space.com is the premier source of space exploration, innovation and astronomy news, chronicling (and celebrating) humanity's ongoing expansion across the final frontier. Originally founded in 1999, Space.com is, and always has been, the passion of writers and editors who are space fans and also trained journalists. Our current news team consists of Editor-in-Chief Tariq Malik; Editor Hanneke Weitering, Senior Space Writer Mike Wall; Senior Writer Meghan Bartels; Senior Writer Chelsea Gohd, Senior Writer Tereza Pultarova and Staff Writer Alexander Cox, focusing on e-commerce. Senior Producer Steve Spaleta oversees our space videos, with Diana Whitcroft as our Social Media Editor.
