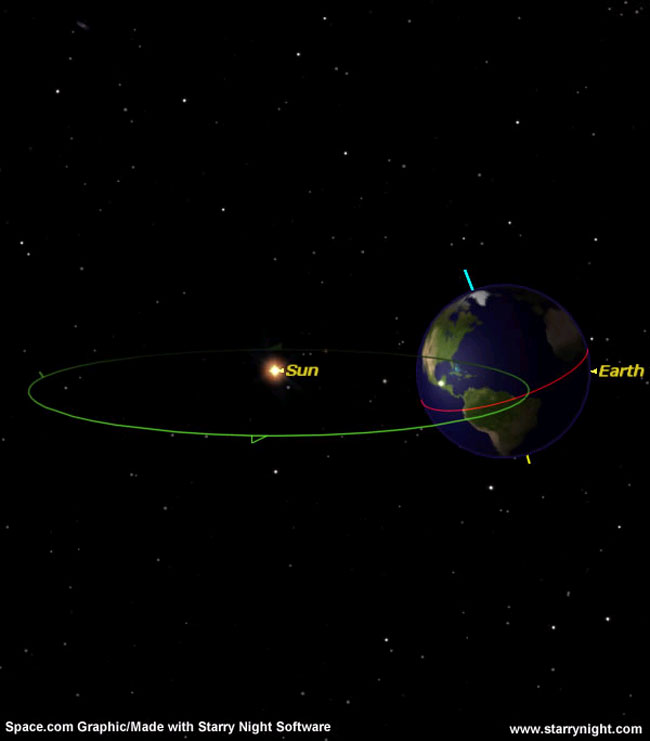
The sun will reach the point where it appears to shine farthest to the north of the equator, over the Tropic of Cancer, today (June 21), marking the moment of the summer solstice — the start of northern summer.
Since Dec. 21, the altitude of the midday sun has been shifting progressively higher in the sky as its direct rays have been gradually migrating to the north. It reached its peak at 1:04 a.m. EDT (0504 GMT), marking the summer solstice.
The sun's altitude above the horizon at noontime is 47 degrees higher now, compared to six months ago. As we often mention, your clenched fist held at arm's length measures roughly 10 degrees, so the sun at midday is now nearly "five fists" higher in the southern sky compared to Dec. 21. [Solar Quiz: How Well Do You Know the Sun]
As "armistice" is defined as a staying of the action of arms, "solstice" is a staying of the sun's apparent motion over the latitudes of the Earth. During the northern summer solstice, the sun stops its northward motion and begins heading south. At the winter solstice, it turns north.
While the June 21 solstice marks the start of summer in the Northern Hemisphere, it is the start of winter in the Southern Hemisphere. Technically, at one minute past the moment of the solstice, the sun has turned around and started south. It will cross the equator at the autumnal equinox, passing into the Southern Hemisphere on Sep. 22, at 4:44 p.m. EDT (2044 GMT).
From temperate latitudes, the sun can never appear directly overhead. From New York, for instance, on Friday at 12:57 p.m. EDT (1657 GMT), the sun will attain its highest point in the sky for this entire year, standing 73 degrees above the southern horizon. Since the Sun will appear to describe such a high arc across the sky, the duration of daylight is now at its most extreme, lasting 15 hours and 4 minutes.
However, contrary to popular belief, the earliest sunrise and latest sunset do not coincide with the summer solstice. In fact, the earliest sunrise actually occurred back on June 14, while the latest sunset is not due until June 27.
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
During the year varying amounts of sunlight strike different regions of the planet and as a consequence both the angle of the sun's path across the sky and the number of hours it is above the horizon change significantly. If the total energy received from the sun — known as insolation — alone governed the temperature, we should now be experiencing the year's hottest weather.
But the atmosphere in temperate regions continues to receive more heat than it gives up to space, a situation that lasts several weeks or more. A reverse process occurs after the winter solstice in late December. Thus, there is a temperature lag of roughly about a month: Our hottest weather usually comes in late July and our coldest in late January.
Joe Rao serves as an instructor and guest lecturer at New York's Hayden Planetarium. He writes about astronomy for Natural History magazine, the Farmer's Almanac and other publications, and he is also an on-camera meteorologist for News 12 Westchester, N.Y. Follow us on Twitter, Facebook and Google+. Original article on SPACE.com.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.

Joe Rao is Space.com's skywatching columnist, as well as a veteran meteorologist and eclipse chaser who also serves as an instructor and guest lecturer at New York's Hayden Planetarium. He writes about astronomy for Natural History magazine, Sky & Telescope and other publications. Joe is an 8-time Emmy-nominated meteorologist who served the Putnam Valley region of New York for over 21 years. You can find him on Twitter and YouTube tracking lunar and solar eclipses, meteor showers and more. To find out Joe's latest project, visit him on Twitter.
