Before and after satellite images show lakes appearing across Sahara after deluge of rain soaks desert
Lakes appearing in the Sahara desert captured in satellite images after a cyclone dumped a years' worth of rain on northern Africa in just a few days.

Lakes have appeared in the Sahara after a cyclone brought a deluge of rain to northern Africa that drenched swathes of the largest hot desert on Earth, satellite images show.
An extratropical cyclone hit parts of Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia and Libya on Sept. 7 and 8, dropping around 8 inches (20 centimeters) on the affected areas — equivalent to an entire year's worth of rainfall in just a few days, according to NASA's Earth Observatory.
The deluge and runoff filled multiple ephemeral lakes in the Sahara, including the Sebkha el Melah in Algeria and several dotted around the Erg Chebbi — a vast expanse of star dunes in Morocco. NASA's Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on the Terra satellite also captured several ephemeral lakes appearing across parts of Morocco and Algeria.
The Erg Chebbi lakes filled after rivers from the nearby Atlas Mountains overflowed close to Merzouga, a town near the Algerian border that serves as a gateway to the star dunes. An image captured on Oct. 1 by one of the Copernicus Sentinel-2 satellites shows new lakes dotted around the edges of Erg Chebbi.
Related: How Earth's Orbit Shaped the Sahara
NASA's Landsat 9 satellite captured the images of the newly filled Sebkha el Melah lake in Algeria. Images captured on Aug. 12 and Sept. 29 and shared by Earth Observatory show changes to the landscape, with a green lake appearing in the desert.

The lake covered 74 square miles (191 square kilometers) and was approximately 7.2 feet (2.2 meters) deep, according to calculations by Moshe Armon, a senior lecturer at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem. Armon used satellite images to establish the extent of the water combined with a 3D map of the lake, according to Earth Observatory.
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
Since 2000, there have been two times when water levels at Sebkha el Melah were higher than they are now. In 2008, the lake filled after an extratropical cyclone that led to exceptionally heavy rainfall. It took four years for the lake to completely dry up again.
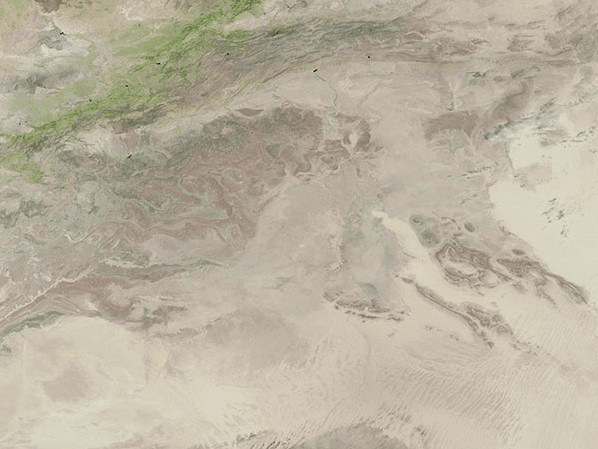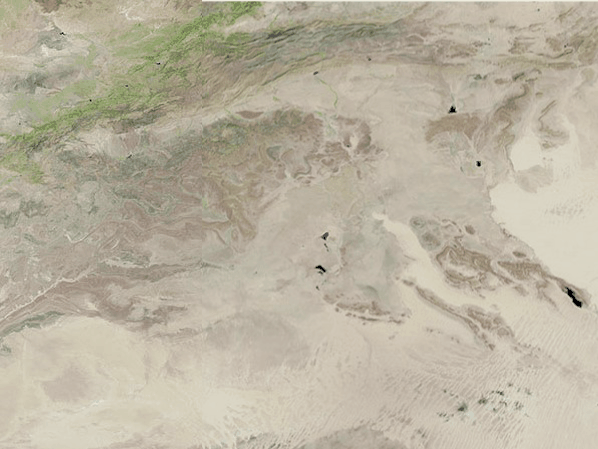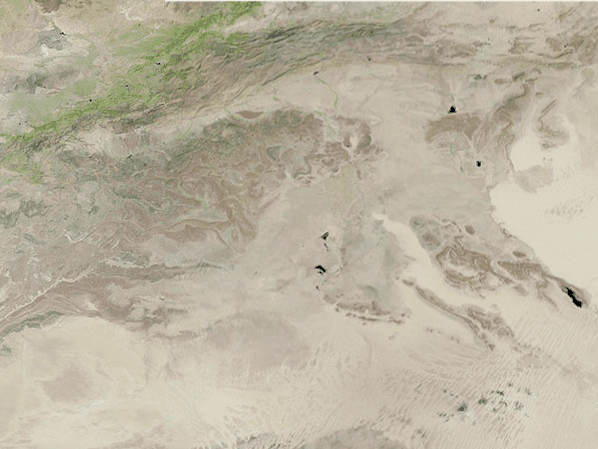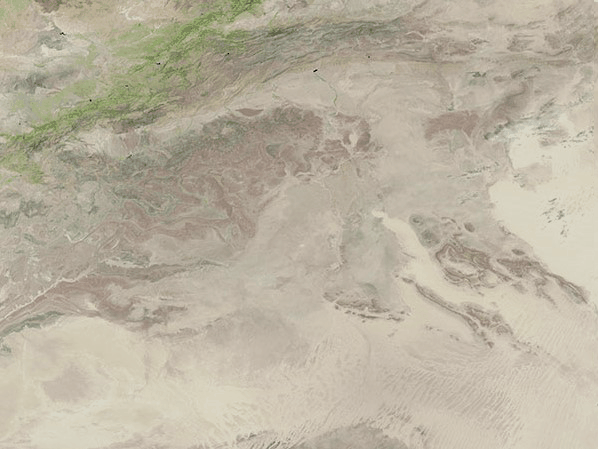
The water currently filling Sebkha el Melah will likely remain for some time. "If we don't get any more rain events, a 2.2-meter depth, like we have now, would take about a year to evaporate completely," Armon said in the statement.
Understanding how rainfall events like the cyclone in September impact the Sahara help researchers better understand what the desert was like thousands of years ago, when it was green, and how it will change in the future as a result of climate change.
Current projections suggest parts of the Sahara will receive more rainfall, but there are huge uncertainties. "What's going to happen in the Sahara remains very unclear, but we hope that we'll eventually develop a better understanding of the Sahara's future by studying these lake-filling events," Armon said.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.
Hannah Osborne is the Earth and Animal Editor at Live Science. Prior to Live Science, she worked for several years at Newsweek as the Science Editor.
-
Helio I assume these revealed locations are ideal for archeologist's and anthropologist's digs.Reply