This Alien World Is the 1st Cloudless Exoplanet Ever Discovered
In a first, an international team of scientists has discovered an exoplanet with no clouds.
The team, led by Nikolay Nikolov, an astronomer at the University of Exeter in the United Kingdom, detected this hot gas giant, known as WASP-96b, using the European Southern Observatory's Very Large Telescope in Chile. The team determined the atmospheric makeup of the exoplanet by studying it as it passed in front of its host star and measuring how the planet and its atmosphere affected light from the star.
A planet's atmospheric makeup influences the light that scientists can measure as it passes by its host star. This creates a spectrum, which is like a unique fingerprint. Typically, clouds obscure the light released by a planet and affect the spectrum that researchers can study from Earth, according to a statement released yesterday (May 7) by the University of Exeter. [The Biggest Mysteries of Saturn]
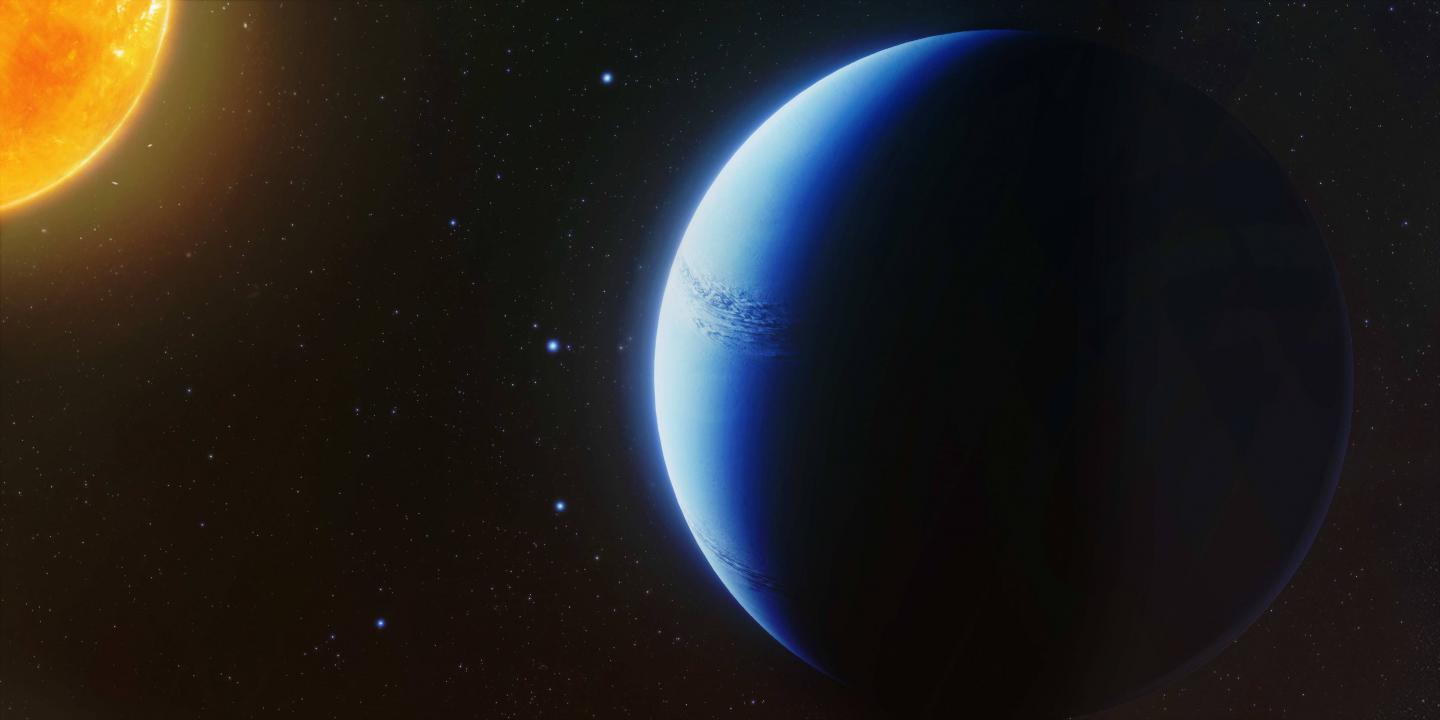

But for WASP-96b, an extremely clear signature for the element sodium was observed. Because clouds typically obscure such signatures, the clarity of this spectrum suggested that the planet's atmosphere has no clouds at all. With its his is the first evidence of an entirely cloudless planet and the first time a planet with such a clear sodium signature has been found, the researchers said.With its uniquely clear signature, WASP-96b is the first-ever cloudless planet discovered. Being the first of its kind, the exoplanet is now considered "a benchmark for characterization," Nikolov said in the statement.
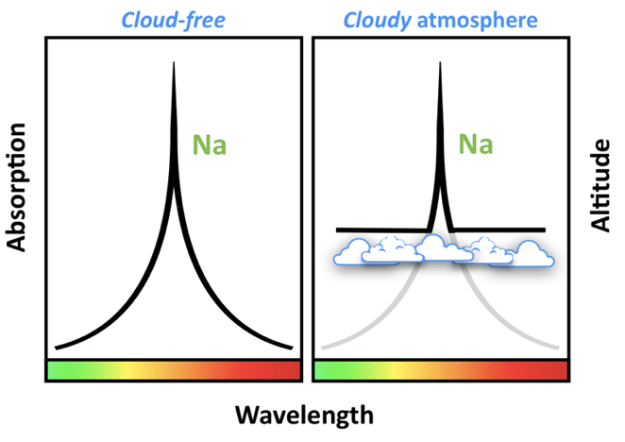
This characterizing spectrum appears in the shape of a camping tent. This uncommon and easy-to-identify shape had never been seen before "because the characteristic 'tent-shaped' profile can only be produced deep in the atmosphere," Nikolov said. He added that for most planets, clouds get in the way, making this shape difficult to discern.
Aside from having an unusually cloudless, sodium-rich atmosphere, WASP-96b is extremely hot, at 1,300 kelvins (1,900 degrees Fahrenheit, or 1,000 degrees Celsius), and extremely large — 20 percent larger than Jupiter. The planet's mass is similar to Saturn's, so researchers classify the alien world as a "hot Saturn."
In addition, the sodium levels in WASP-96b's atmosphere are similar to those found throughout our solar system. Sodium is the seventh most abundant element in the universe, and for a long time, scientists have thought that large gas giants had sodium-rich atmospheres, according to the statement. But until now, such clear evidence to support this idea has not existed, so the observance of WASP-96b solidifies scientists' understanding of gas giants.
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
Because of WASP-96b's cloudless skies, studying the exoplanet will provide researchers with a "unique opportunity to determine the abundances of other molecules, such as water, carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide, with future observations," Ernst de Mooij,a researcher at Dublin City University and a co-author of a new study describing the findings, said in the statement.
So, by identifying the signatures of other molecules using telescopes like Hubble and the upcoming James Webb Space Telescope, scientists can gain a better understanding of planets both within and outside our solar system, the researchers said.
The new work was detailed yesterday (May 7) in the journal Nature.
Email Chelsea Gohd at cgohd@space.com or follow her @chelsea_gohd. Follow us @Spacedotcom, Facebook and Google+. Original article on Space.com.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.

Chelsea “Foxanne” Gohd joined Space.com in 2018 and is now a Senior Writer, writing about everything from climate change to planetary science and human spaceflight in both articles and on-camera in videos. With a degree in Public Health and biological sciences, Chelsea has written and worked for institutions including the American Museum of Natural History, Scientific American, Discover Magazine Blog, Astronomy Magazine and Live Science. When not writing, editing or filming something space-y, Chelsea "Foxanne" Gohd is writing music and performing as Foxanne, even launching a song to space in 2021 with Inspiration4. You can follow her on Twitter @chelsea_gohd and @foxannemusic.